Adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation for acute liver failure in China
- PMID: 23326128
- PMCID: PMC3544025
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7234
Adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation for acute liver failure in China
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the long-term outcome of recipients and donors of adult-to-adult living-donor liver transplantation (AALDLT) for acute liver failure (ALF).
Methods: Between January 2005 and March 2010, 170 living donor liver transplantations were performed at West China Hospital of Sichuan University. All living liver donor was voluntary and provided informed consent. Twenty ALF patients underwent AALDLT for rapid deterioration of liver function. ALF was defined based on the criteria of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, including evidence of coagulation abnormality [international normalized ratio (INR) ≥ 1.5] and degree of mental alteration without pre-existing cirrhosis and with an illness of < 26 wk duration. We reviewed the clinical indications, operative procedure and prognosis of AALDTL performed on patients with ALF and corresponding living donors. The potential factors of recipient with ALF and corresponding donor outcome were respectively investigated using multivariate analysis. Survival rates after operation were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method. Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was undertaken to identify the threshold of potential risk factors.
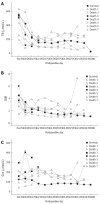
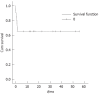
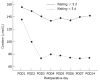
Results: The causes of ALF were hepatitis B (n = 18), drug-induced (n = 1) and indeterminate (n = 1). The score of the model for end-stage liver disease was 37.1 ± 8.6, and the waiting duration of recipients was 5 ± 4 d. The graft types included right lobe (n = 17) and dual graft (n = 3). The mean graft weight was 623.3 ± 111.3 g, which corresponded to graft-to-recipient weight ratio of 0.95% ± 0.14%. The segment Vor VIII hepatic vein was reconstructed in 11 right-lobe grafts. The 1-year and 3-year recipient's survival and graft survival rates were 65% (13 of 20). Postoperative results of total bilirubin, INR and creatinine showed obvious improvements in the survived patients. However, the creatinine level of the deaths was increased postoperatively and became more aggravated compared with the level of the survived recipients. Multivariate analysis showed that waiting duration was independently correlated with increased mortality (P = 0.014). Furthermore, ROC curve revealed the cut-off value of waiting time was 5 d (P = 0.011, area under the curve = 0.791) for determining the mortality. The short-term creatinine level with different recipient's waiting duration was described. The recipients with waiting duration ≥ 5 d showed the worse renal function and higher mortality than those with waiting duration < 5 d (66.7% vs 9.1%, P = 0.017). In addition, all donors had no residual morbidity. Furthermore, univariate analysis did not show that short assessment time induced the high morbidity (P = 0.573).
Conclusion: Timely AALDLT for patients with ALF greatly improves the recipient survival. However, further systemic review is needed to investigate the optimal treatment strategy for ALF.
Keywords: Acute liver failure; Adult-to-adult liver donor liver transplantation; Donor; Recipient; Risk factors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Live donor liver transplantation for acute liver failure: A single center experience.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jan;37(1):25-30. doi: 10.1007/s12664-017-0812-y. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29455437
-
[Analysis of fifty adult to adult living donor liver transplantation].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2007 Jun;38(3):513-7. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2007. PMID: 17593845 Chinese.
-
Liver transplantation for acute liver failure: are there thresholds not to be crossed?Transpl Int. 2014 Jun;27(6):625-33. doi: 10.1111/tri.12302. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Transpl Int. 2014. PMID: 24606197
-
Management of the middle hepatic vein and its tributaries in right lobe living donor liver transplantation.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007 Aug;6(4):358-63. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007. PMID: 17690029 Review.
-
Mechanisms and aetiology-dependent treatment of acute liver failure.Liver Int. 2025 Mar;45(3):e15739. doi: 10.1111/liv.15739. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Liver Int. 2025. PMID: 37752801 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Live donor liver transplantation for acute liver failure: A single center experience.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jan;37(1):25-30. doi: 10.1007/s12664-017-0812-y. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29455437
-
Pre-transplant predictors of 3-Month survival following liver transplantation for acute liver failure in adult and pediatric patients in Türkiye.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 19;15(1):26221. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11298-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40683961 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Modified Sini Decoction on Survival Rates of Patients with Hepatitis B Virus Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Feb 24;2019:2501847. doi: 10.1155/2019/2501847. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 30915144 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effect of double plasma molecular adsorption system and sequential half-dose plasma exchange in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure.J Clin Apher. 2019 Aug;34(4):392-398. doi: 10.1002/jca.21690. Epub 2019 Feb 13. J Clin Apher. 2019. PMID: 30758886 Free PMC article.
-
Acute liver failure and liver transplantation.Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2013 Aug;2(3):77-87. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2013.v2.3.77. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2013. PMID: 25343108 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Polson J, Lee WM. AASLD position paper: the management of acute liver failure. Hepatology. 2005;41:1179–1197. - PubMed
-
- Park SJ, Lim YS, Hwang S, Heo NY, Lee HC, Suh DJ, Yu E, Lee SG. Emergency adult-to-adult living-donor liver transplantation for acute liver failure in a hepatitis B virus endemic area. Hepatology. 2010;51:903–911. - PubMed
-
- Shi-Chun L, Meng-Long W, Ning L, Wei L, Ping C, Jin-Ning L, Jun D, Zhen Z, Ju-Shan W, Dong-Dong L, et al. Emergent right lobe adult-to-adult living-donor liver transplantation for high model for end-stage liver disease score severe hepatitis. Transpl Int. 2010;23:23–30. - PubMed
-
- Ikegami T, Taketomi A, Soejima Y, Yoshizumi T, Sanefuji K, Kayashima H, Shimada M, Maehara Y. Living donor liver transplantation for acute liver failure: a 10-year experience in a single center. J Am Coll Surg. 2008;206:412–418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

