Highlights for α-fetoprotein in determining prognosis and treatment monitoring for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 23326129
- PMCID: PMC3544026
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7242
Highlights for α-fetoprotein in determining prognosis and treatment monitoring for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: To explore the prognostic value in the monitoring of treatment efficacy of serial α-fetoprotein (AFP) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients.
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE and COCHRANE LIBRARY through April 21, 2012, to find qualifying articles. Our overall search strategy included terms for HCC, AFP, treatment response, and prognosis. Literature was limited to English-language, human studies. Studies reporting cumulative survival rates were summarized qualitatively. For the prognostic meta-analysis, we undertook a series of meta-analyses that summarised the Cox proportional hazard ratios (HRs) by assuming a random effects model. With regards to the correlation of AFP change with radiologic response, the categorical dichotomous variables were assessed using Poisson relative risks (RRs), which were incorporated into the random effects model meta-analysis of accuracy prediction. Between-study heterogeneity was estimated by use of the I² statistic. Publication bias was evaluated using the Begg funnel plot and Egger plot. Sensitivity analyses were conducted first by separating systemic treatment estimates from locoregional therapy estimates, evaluating different AFP response cut-off point effects, and exploring the impact of different study sizes.
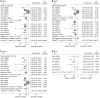
Results: Of 142 titles identified in our original search, 11 articles (12 clinical studies) met our criteria. Six studies investigated outcome in a total of 464 cases who underwent systemic treatment, and six studies investigated outcome in a total of 510 patients who received locoregional therapy. A random-effects model meta-analysis showed that AFP response was associated with an mortality HR of 0.55 (95%CI, 0.47-0.65) across HCC in overall survival (OS) and 0.50 (95%CI, 0.38-0.65) in progression-free survival. Restricting analysis to the six eligible analyses of systemic treatment, the pooled HRs were 0.64 (95%CI, 0.53-0.77) for OS. Limiting analysis to the six analyses of locoregional therapy, the pooled HRs for OS was 0.39 (95%CI, 0.29-0.53). We showed a larger pooled HR in the 50% definition studies (HR, 0.67, 95%CI, 0.55-0.83) compared with that from the 20% definition studies (HR, 0.41, 95%CI, 0.32-0.53). Restricting analysis to the four studies including over 100 patients individually, the pooled HR was 0.65 (95%CI, 0.54-0.79), with a pooled HR for OS of 0.35 (95%CI, 0.23-0.46) in the studies of less than 100 patients. As to radiological imaging, 43.1% (155/360) of the patients in the AFP response group presented with a radiological overall response, while the response rate decreased to 11.5% (36/313) in the patients from the AFP nonresponse group. The RR of having no overall response was significantly lower in the AFP response group than the AFP nonresponse group (RR, 0.67; 95%CI, 0.61-0.75). In terms of disease control rate, 86.9% (287/330) in the AFP response group and 51.0% (153/300) in the AFP nonresponse group showed successful disease control, respectively. The RR of disease control failure, similarly, was significantly lower in the AFP response group (RR, 0.37; 95%CI, 0.23-0.58). But these findings could be overestimates because of publication and reporting bias.
Conclusion: HCC patients presenting with an AFP response are at decreased risk of mortality. In addition, patients with an AFP response also present with a higher overall response rate and disease control rate.
Keywords: Liver cancer; Monitoring; Prognosis; Response; α-fetoprotein.
Figures

References
-
- Venook AP, Papandreou C, Furuse J, de Guevara LL. The incidence and epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: a global and regional perspective. Oncologist. 2010;15 Suppl 4:5–13. - PubMed
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245–1255. - PubMed
-
- Singal AG, Marrero JA. Recent advances in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2010;26:189–195. - PubMed
-
- Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van Oosterom AT, Christian MC, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:205–216. - PubMed
-
- Padhani AR, Ollivier L. The RECIST (Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors) criteria: implications for diagnostic radiologists. Br J Radiol. 2001;74:983–986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

