Delayed liver laceration following transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for portal hypertension
- PMID: 23326153
- PMCID: PMC3544050
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7405
Delayed liver laceration following transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for portal hypertension
Abstract
The transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is an acceptable procedure that has proven benefits in the treatment of patients who have complications from portal hypertension due to liver cirrhosis. Delayed liver laceration is a rare complication of the TIPS procedure. We describe a patient with portal hypertension due to liver cirrhosis, who suddenly presented with abdominal hemorrhage and liver laceration 8 d after TIPS. Few reports have described complications after TIPS placement. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report describing delayed liver laceration. This potential and serious complication appears to be specific and fatal for TIPS in portal hypertension. We advocate careful attention to the technique to avoid this complication, and timely treatment is extremely important.
Keywords: Hemorrhage; Liver cirrhosis; Portal hypertension; Postoperative complications; Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
Figures

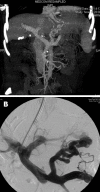
Comment in
-
Reducing risk of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt using ultrasound guided single needle pass.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jun 14;19(22):3528-30. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i22.3528. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23801852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyer TD, Haskal ZJ. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Practice Guidelines: the role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation in the management of portal hypertension. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005;16:615–629. - PubMed
-
- Boyer TD, Haskal ZJ. The Role of Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) in the Management of Portal Hypertension: update 2009. Hepatology. 2010;51:306. - PubMed
-
- Bilbao JI, Quiroga J, Herrero JI, Benito A. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS): current status and future possibilities. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2003;25:251–269. - PubMed
-
- Wu X, Ding W, Cao J, Han J, Huang Q, Li N, Li J. Favorable clinical outcome using a covered stent following transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in patients with portal hypertension. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010;17:701–708. - PubMed
-
- Wu X, Han J, Cao J, Wu X, Li W, Sun J, Li J. Combined TIPS with portal-azygous disconnection improved the long term clinical outcome in portal hypertension patients. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2009;16:858–864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

