Comparison of different intraocular pressure measurement techniques in normal eyes, post surface and post lamellar refractive surgery
- PMID: 23326186
- PMCID: PMC3544333
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S37978
Comparison of different intraocular pressure measurement techniques in normal eyes, post surface and post lamellar refractive surgery
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to determine the accuracy of intraocular pressure (IOP) measurement after laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) or epithelial laser in situ keratomileusis (Epi)-LASIK using Goldmann applanation tonometry, air puff tonometry, ocular response analyzer corneal compensated IOP (ORA IOPcc) and Pentacam corrected IOP.
Methods: A prospective comparative clinical study was conducted between February and September 2011 on 30 eyes divided into four groups, i.e. 20 corneas of 10 patients before LASIK (group A), 20 corneas of the same patients 2 months postoperatively (group B), 10 corneas of five patients before Epi-LASIK (group C), and 10 corneas of the same patients 2 months postoperatively (group D). Patient age ranged from 20 to 50 years. IOP was measured using Goldmann applanation and air puff tonometry, ORA corneal compensation, and Pentacam correction (which also measured central corneal thickness).
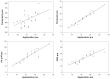
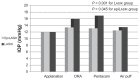
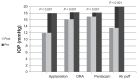
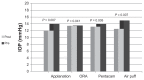
Results: Significant positive linear correlations were found between IOP values measured by Goldmann applanation tonometry and other techniques, and with preoperative pachymetry in group A. The correlation between preoperative Pentacam-corrected and preoperative ORA corneal-compensated IOP was strongest for Goldmann applanation tonometry (r = 0.97 and r = 0.858 respectively, P < 0.001). Compared with preoperative values, postoperative IOP measured by the four methods were significantly lower. The difference was statistically significant when IOP was measured using Goldmann applanation and air puff tonometry compared with the ORA and Pentacam methods (P < 0.001 for LASIK patients and P = 0.017 for Epi-LASIK patients). Nonsignificant correlations were found between the degree of lowering of postoperative IOP and postoperative pachymetry in groups B and D.
Conclusion: Refractive surgery causes significant lowering of IOP as measured using Goldmann applanation tonometry, air puff tonometry, ORA compensation, and Pentacam correction. LASIK has a greater effect than Epi-LASIK on IOP measurement error following refractive surgery.
Keywords: corneal biomechanics; corneal thickness; intraocular pressure measurement; refractive surgery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Measurement of intraocular pressure in LASIK and LASEK patients using the Reichert Ocular Response Analyzer and Goldmann applanation tonometry.J Refract Surg. 2008 Apr;24(4):366-70. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20080401-09. J Refract Surg. 2008. PMID: 18500086
-
Changes in biomechanical properties of the cornea and intraocular pressure after myopic laser in situ keratomileusis using a femtosecond laser for flap creation determined using ocular response analyzer and Goldmann applanation tonometry.J Glaucoma. 2015 Mar;24(3):195-201. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e31829da1ec. J Glaucoma. 2015. PMID: 23807345
-
Refinement of Intraocular Pressure Measurements made by Ocular Response Analyzer following Laser in Situ Keratomileusis using M2 90 Moria Microkeratome for Egyptian Myopic and Astigmatic Patients.Electron Physician. 2016 Dec 25;8(12):3429-3433. doi: 10.19082/3429. eCollection 2016 Dec. Electron Physician. 2016. PMID: 28163860 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of intraocular pressure measured by ocular response analyzer and Goldmann applanation tonometer after corneal refractive surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Ophthalmol. 2020 Jan 10;20(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12886-019-1288-6. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31924174 Free PMC article.
-
Finite element simulation of Goldmann tonometry after refractive surgery.Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2020 Jan;71:24-28. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2019.09.007. Epub 2019 Oct 5. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2020. PMID: 31677547
Cited by
-
Comparison of different correction formulas and measurement methods for the accurate determination of intraocular pressure after SMILE and FS-LASIK surgery.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 Oct 10;22(1):404. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02620-7. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36217120 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hemifacial Spasm on Intraocular Pressure Measurement.J Ophthalmol. 2018 Feb 6;2018:3621215. doi: 10.1155/2018/3621215. eCollection 2018. J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29545951 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of different intraocular pressure measurement techniques in normal eyes and post small incision lenticule extraction.Clin Ophthalmol. 2017 Jul 14;11:1309-1314. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S132578. eCollection 2017. Clin Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28761329 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Intraocular Pressure before and after Laser In Situ Keratomileusis Refractive Surgery Measured with Perkins Tonometry, Noncontact Tonometry, and Transpalpebral Tonometry.J Ophthalmol. 2015;2015:683895. doi: 10.1155/2015/683895. Epub 2015 Jun 8. J Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 26167293 Free PMC article.
-
Intraocular pressure after myopic laser refractive surgery measured with a new Goldmann convex prism: correlations with GAT and ORA.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 Feb 16;22(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02309-x. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35168601 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grødum K, Heijl A, Bengtsson B. A comparison of glaucoma patients identified through mass screening and in routine clinical practice. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2002;80:627–631. - PubMed
-
- Kass MA, Heuer DK, Higginbotham EJ, et al. The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study: a randomized trial determines that topical ocular hypotensive medication delays or prevents the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120:701–713. - PubMed
-
- Bengtsson B, Leske MC, Hyman L, Heijl A Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial Group. Fluctuation of intraocular pressure and glaucoma progression in the early manifest glaucoma trial. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:205–209. - PubMed
-
- Pepose JS, Feigenbaum SK, Qazi MA, et al. Changes in corneal biomechanics and intraocular pressure following LASIK using static, dynamic, and noncontact tonometry. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007;143:39–47. - PubMed
-
- Whitacre MM, Stein R. Sources of errors with use of Goldmann-type tonometers. Surv Ophthalmol. 1993;38:1–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

