Teleost fish mount complex clonal IgM and IgT responses in spleen upon systemic viral infection
- PMID: 23326228
- PMCID: PMC3542120
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003098
Teleost fish mount complex clonal IgM and IgT responses in spleen upon systemic viral infection
Abstract
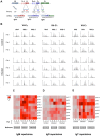
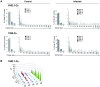
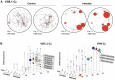
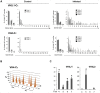
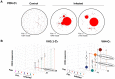
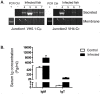
Upon infection, B-lymphocytes expressing antibodies specific for the intruding pathogen develop clonal responses triggered by pathogen recognition via the B-cell receptor. The constant region of antibodies produced by such responding clones dictates their functional properties. In teleost fish, the clonal structure of B-cell responses and the respective contribution of the three isotypes IgM, IgD and IgT remain unknown. The expression of IgM and IgT are mutually exclusive, leading to the existence of two B-cell subsets expressing either both IgM and IgD or only IgT. Here, we undertook a comprehensive analysis of the variable heavy chain (VH) domain repertoires of the IgM, IgD and IgT in spleen of homozygous isogenic rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss) before, and after challenge with a rhabdovirus, the Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus (VHSV), using CDR3-length spectratyping and pyrosequencing of immunoglobulin (Ig) transcripts. In healthy fish, we observed distinct repertoires for IgM, IgD and IgT, respectively, with a few amplified μ and τ junctions, suggesting the presence of IgM- and IgT-secreting cells in the spleen. In infected animals, we detected complex and highly diverse IgM responses involving all VH subgroups, and dominated by a few large public and private clones. A lower number of robust clonal responses involving only a few VH were detected for the mucosal IgT, indicating that both IgM(+) and IgT(+) spleen B cells responded to systemic infection but at different degrees. In contrast, the IgD response to the infection was faint. Although fish IgD and IgT present different structural features and evolutionary origin compared to mammalian IgD and IgA, respectively, their implication in the B-cell response evokes these mouse and human counterparts. Thus, it appears that the general properties of antibody responses were already in place in common ancestors of fish and mammals, and were globally conserved during evolution with possible functional convergences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Burnet FM (1957) A modification of Jerne's theory of antibody production using the concept of clonal selection. Aust J Sci 20: 67–70. - PubMed
-
- Flajnik MF, Du Pasquier L (2008) Evolution of the immune system. In: Paul W, editor. Fundamental Immunology. 6th edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott and Wolters Kluwer. pp. 56–125.
-
- Zwollo P, Cole S, Bromage E, Kaattari S (2005) B cell heterogeneity in the teleost kidney: evidence for a maturation gradient from anterior to posterior kidney. J Immunol 174: 6608–6616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

