Lipid exchange between Borrelia burgdorferi and host cells
- PMID: 23326230
- PMCID: PMC3542181
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003109
Lipid exchange between Borrelia burgdorferi and host cells
Abstract
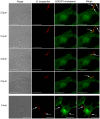
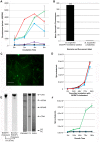
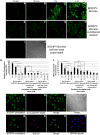
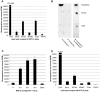
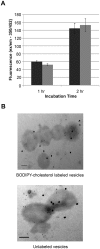
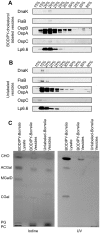
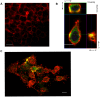
Borrelia burgdorferi, the agent of Lyme disease, has cholesterol and cholesterol-glycolipids that are essential for bacterial fitness, are antigenic, and could be important in mediating interactions with cells of the eukaryotic host. We show that the spirochetes can acquire cholesterol from plasma membranes of epithelial cells. In addition, through fluorescent and confocal microscopy combined with biochemical approaches, we demonstrated that B. burgdorferi labeled with the fluorescent cholesterol analog BODIPY-cholesterol or (3)H-labeled cholesterol transfer both cholesterol and cholesterol-glycolipids to HeLa cells. The transfer occurs through two different mechanisms, by direct contact between the bacteria and eukaryotic cell and/or through release of outer membrane vesicles. Thus, two-way lipid exchange between spirochetes and host cells can occur. This lipid exchange could be an important process that contributes to the pathogenesis of Lyme disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cholesterol lipids of Borrelia burgdorferi form lipid rafts and are required for the bactericidal activity of a complement-independent antibody.Cell Host Microbe. 2010 Oct 21;8(4):331-42. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2010.09.001. Cell Host Microbe. 2010. PMID: 20951967 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA transcript distribution bias between Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria and their outer membrane vesicles.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018 Jul 1;365(13):fny135. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fny135. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29846577 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi Binding to Mammalian Cells and Extracellular Matrix.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1690:57-67. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7383-5_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29032536 Free PMC article.
-
Immune responses induced by spirochetal outer membrane lipoproteins and glycolipids.Immunobiology. 2008;213(3-4):329-40. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2007.11.003. Epub 2008 Jan 2. Immunobiology. 2008. PMID: 18406378 Review.
-
Borrelia burgdorferi hijacks cellular metabolism of immune cells: Consequences for host defense.Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020 May;11(3):101386. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2020.101386. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020. PMID: 32035898 Review.
Cited by
-
Borrelia burgdorferi Outer Membrane Vesicles Contain Antigenic Proteins, but Do Not Induce Cell Death in Human Cells.Microorganisms. 2022 Jan 19;10(2):212. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020212. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35208666 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenicity and virulence of Borrelia burgdorferi.Virulence. 2023 Dec;14(1):2265015. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2023.2265015. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Virulence. 2023. PMID: 37814488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The intracellular bacteria Chlamydia hijack peroxisomes and utilize their enzymatic capacity to produce bacteria-specific phospholipids.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 23;9(1):e86196. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086196. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465954 Free PMC article.
-
Cell lipid biology in infections: an overview.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Oct 6;13:1148383. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1148383. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37868347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of cholesterol analogues bearing BODIPY fluorophores by Suzuki or Liebeskind-Srogl cross-coupling and evaluation of their potential for visualization of cholesterol pools.Chembiochem. 2014 Sep 22;15(14):2087-96. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201402042. Epub 2014 Aug 22. Chembiochem. 2014. PMID: 25154602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burgdorfer W, Barbour AG, Hayes SF, Benach JL, Grunwaldt E, et al. (1982) Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science 216: 1317–1319. - PubMed
-
- Benach JL, Bosler EM, Hanrahan JP, Coleman JL, Habicht GS, et al. (1983) Spirochetes isolated from the blood of two patients with Lyme disease. N Engl J Med 308: 740–742. - PubMed
-
- Hossain H, Wellensiek HJ, Geyer R, Lochnit G (2001) Structural analysis of glycolipids from Borrelia burgdorferi. Biochimie 83: 683–692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

