A Drosophila model of high sugar diet-induced cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 23326243
- PMCID: PMC3542070
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003175
A Drosophila model of high sugar diet-induced cardiomyopathy
Abstract
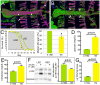
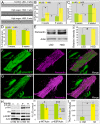
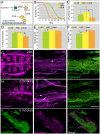
Diets high in carbohydrates have long been linked to progressive heart dysfunction, yet the mechanisms by which chronic high sugar leads to heart failure remain poorly understood. Here we combine diet, genetics, and physiology to establish an adult Drosophila melanogaster model of chronic high sugar-induced heart disease. We demonstrate deterioration of heart function accompanied by fibrosis-like collagen accumulation, insulin signaling defects, and fat accumulation. The result was a shorter life span that was more severe in the presence of reduced insulin and P38 signaling. We provide evidence of a role for hexosamine flux, a metabolic pathway accessed by glucose. Increased hexosamine flux led to heart function defects and structural damage; conversely, cardiac-specific reduction of pathway activity prevented sugar-induced heart dysfunction. Our data establish Drosophila as a useful system for exploring specific aspects of diet-induced heart dysfunction and emphasize enzymes within the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway as candidate therapeutic targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Marriott BP, Cole N, Lee E (2009) National Estimates of Dietary Fructose Intake Increased from 1977 to 2004 in the United States. The Journal of Nutrition 139: 1228S–1235S. - PubMed
-
- Mellor KM, Ritchie RH, Davidoff AJ, Delbridge LMD (2010) Elevated dietary sugar and the heart: experimental models and myocardial remodeling. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 88: 525–540. - PubMed
-
- Selvin E, Coresh J, Golden SH, Brancati FL, Folsom AR, et al. (2005) Glycemic Control and Coronary Heart Disease Risk in Persons With and Without Diabetes: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Arch Intern Med 165: 1910–1916. - PubMed
-
- Rubler S, Dlugash J, Yuceoglu YZ, Kumral T, Branwood AW, et al. (1972) New type of cardiomyopathy associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. The American Journal of Cardiology 30: 595–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- (#NIH/NHLBI RO1 HL54732-16/PHS HHS/United States
- F32 DK098053/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM062754/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL054732/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085481-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- #R24 DK098053/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5K12HD001459-12/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG033561/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG033561-02/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL0980539-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM062754/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD001459/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085481/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007464/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

