Genome-wide screens for in vivo Tinman binding sites identify cardiac enhancers with diverse functional architectures
- PMID: 23326246
- PMCID: PMC3542182
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003195
Genome-wide screens for in vivo Tinman binding sites identify cardiac enhancers with diverse functional architectures
Abstract
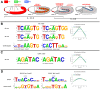
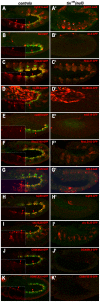
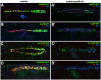
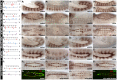
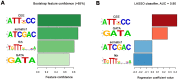
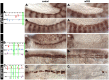
The NK homeodomain factor Tinman is a crucial regulator of early mesoderm patterning and, together with the GATA factor Pannier and the Dorsocross T-box factors, serves as one of the key cardiogenic factors during specification and differentiation of heart cells. Although the basic framework of regulatory interactions driving heart development has been worked out, only about a dozen genes involved in heart development have been designated as direct Tinman target genes to date, and detailed information about the functional architectures of their cardiac enhancers is lacking. We have used immunoprecipitation of chromatin (ChIP) from embryos at two different stages of early cardiogenesis to obtain a global overview of the sequences bound by Tinman in vivo and their linked genes. Our data from the analysis of ~50 sequences with high Tinman occupancy show that the majority of such sequences act as enhancers in various mesodermal tissues in which Tinman is active. All of the dorsal mesodermal and cardiac enhancers, but not some of the others, require tinman function. The cardiac enhancers feature diverse arrangements of binding motifs for Tinman, Pannier, and Dorsocross. By employing these cardiac and non-cardiac enhancers in machine learning approaches, we identify a novel motif, termed CEE, as a classifier for cardiac enhancers. In vivo assays for the requirement of the binding motifs of Tinman, Pannier, and Dorsocross, as well as the CEE motifs in a set of cardiac enhancers, show that the Tinman sites are essential in all but one of the tested enhancers; although on occasion they can be functionally redundant with Dorsocross sites. The enhancers differ widely with respect to their requirement for Pannier, Dorsocross, and CEE sites, which we ascribe to their different position in the regulatory circuitry, their distinct temporal and spatial activities during cardiogenesis, and functional redundancies among different factor binding sites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Bodmer R, Frasch M (2010) Development and aging of the Drosophila heart. In: Harvey R, Rosenthal N, editors. Heart Development and Regeneration. Oxford: Academic Press. pp. 47–86.
-
- Yin Z, Xu X-L, Frasch M (1997) Regulation of the Twist target gene tinman by modular cis-regulatory elements during early mesoderm development. Development 124: 4871–4982. - PubMed
-
- Bodmer R, Jan LY, Jan YN (1990) A new homeobox-containing gene, msh-2, is transiently expressed early during mesoderm formation of Drosophila . Development 110: 661–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

