Differentiating Branch Duct and Mixed IPMN in Endoscopically Collected Pancreatic Cyst Fluid via Cytokine Analysis
- PMID: 23326260
- PMCID: PMC3543798
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/247309
Differentiating Branch Duct and Mixed IPMN in Endoscopically Collected Pancreatic Cyst Fluid via Cytokine Analysis
Abstract
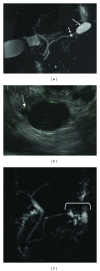
Background. Differentiating branch duct from mixed intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (BD-IPMN) is problematic, but clinically important as mixed IPMNs are managed surgically, while some BD-IPMN may be followed. Inflammatory mediator proteins (IMPs) have been implicated in acute and chronic inflammatory and malignant pancreatic diseases. Aim. To compare IMP profile of pancreatic cyst fluid collected endoscopically from BD-IPMN and mixed IPMN. Methods. Pancreatic cyst fluid from ten patients (5 BD-IPMN and 5 mixed IPMN) was collected by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Concentrations of 89 IMPs in these samples were determined using a multiplexed bead-based microarray protein assay and compared between BD-IPMN and mixed IPMN. Results. Eighty-six of 89 IMPs were detected in at least one of the 10 samples. Fourteen IMPs were detected only in mixed IPMN, while none were only in BD-IPMN. Of these, TGF-β1 was most prevalent, present in 3 of 5 mixed IPMNs. Seventy-two IMPs were detected in both BD-IPMN and mixed IPMNs. Of these, only G-CSF (P < 0.05) was present in higher concentrations in mixed IPMNs. Conclusion. TGF-β1 and G-CSF detected in endoscopically collected pancreatic cyst fluid are potential diagnostic biomarkers capable of distinguishing mixed IPMN from BD-IPMN.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inflammatory protein profiling of pancreatic cyst fluid using EUS-FNA in tandem with cytokine microarray differentiates between branch duct IPMN and inflammatory cysts.J Immunol Methods. 2012 Aug 31;382(1-2):142-149. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2012.05.018. Epub 2012 Jun 7. J Immunol Methods. 2012. PMID: 22683544 Free PMC article.
-
MUC2 expression and prevalence of high-grade dysplasia and invasive carcinoma in mixed-type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas.Pancreatology. 2013 Nov-Dec;13(6):583-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2013.08.007. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Pancreatology. 2013. PMID: 24280573
-
Pancreatic main-duct involvement in branch-duct IPMNs: an underestimated risk.Ann Surg. 2014 Nov;260(5):848-55; discussion 855-6. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000980. Ann Surg. 2014. PMID: 25379856
-
The role of endoscopic ultrasound in the management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.Minerva Med. 2014 Oct;105(5):413-21. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Minerva Med. 2014. PMID: 25000220 Review.
-
The role of endoscopic ultrasound in the management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: a systematic update.Minerva Med. 2016 Dec;107(6):370-380. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Minerva Med. 2016. PMID: 27627636 Review.
Cited by
-
The utilization of imaging features in the management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014;2014:765451. doi: 10.1155/2014/765451. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014. PMID: 25202326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical Intracystic Biomarkers in the Differential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jul 26;58(8):994. doi: 10.3390/medicina58080994. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35893110 Free PMC article.
-
Cyst fluid biomarkers for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a critical review from the international expert meeting on pancreatic branch-duct-intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.J Am Coll Surg. 2015 Feb;220(2):243-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2014.11.001. Epub 2014 Nov 6. J Am Coll Surg. 2015. PMID: 25592469 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lee LS, Saltzman JR, Bounds BC, Poneros JM, Brugge WR, Thompson CC. EUS-guided fine needle aspiration of pancreatic cysts: a retrospective analysis of complications and their predictors. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2005;3(3):231–236. - PubMed
-
- Al Haddad H, Laursen PB, Chollet D, Ahmaidi S, Buchheit M. Reliability of resting and postexercise heart rate measures. International Journal of Sports Medicine. 2011;32(8):598–605. - PubMed
-
- Maker AV, Lee LS, Raut CP, Clancy TE, Swanson RS. Cytology from pancreatic cysts has marginal utility in surgical decision-making. Annals of Surgical Oncology. 2008;15(11):3187–3192. - PubMed
-
- Cannon JG. Inflammatory cytokines in nonpathological states. News in Physiological Sciences. 2000;15(6):298–303. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez EJ, Lolis E. Structure, function, and inhibition of chemokines. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 2002;42:469–499. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

