Herbal Compound "Songyou Yin" Renders Hepatocellular Carcinoma Sensitive to Oxaliplatin through Inhibition of Stemness
- PMID: 23326293
- PMCID: PMC3541605
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/908601
Herbal Compound "Songyou Yin" Renders Hepatocellular Carcinoma Sensitive to Oxaliplatin through Inhibition of Stemness
Abstract
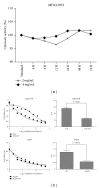
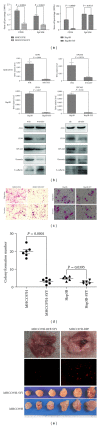
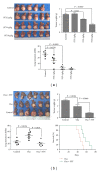
We investigated the effect of Chinese herbal compound Song-you Yin on HCC stemness. MHCC97H and Hep3B cell lines were pretreated with SYY for 4 weeks, and their chemosensitivity to oxaliplatin was evaluated. The expression of CSC-related markers, cell invasion and migration, and colony formation were also examined. SYY-treated orthotopic nude mouse models of human HCC were developed to explore the effect of oxaliplatin on tumor growth, metastasis, and survival. The CSC-related molecular changes in vivo were also evaluated. The result showed that MHCC97H and Hep3B cells pretreated with SYY showed significantly increased chemosensitivity to oxaliplatin and the downregulation of CSC-related markers CD90, CD24, and EPCAM. SYY also attenuated cell motility, invasion, and colony formation in MHCC97H and Hep3B cell lines. The reduced tumorigenicity and pulmonary metastasis were observed in SYY-pretreated cell lines. Combination treatment with oxaliplatin and SYY significantly reduced tumor volume and pulmonary metastasis and prolonged survival compared with oxaliplatin treatment alone. Immunohistochemical analysis showed reduced expression of CD90, ABCG2, ALDH, CD44, EPCAM, vimentin, and MMP-9 and increased the expression of E-cadherin, in HCC cells following combination treatment. These data clearly demonstrate that SYY renders hepatocellular carcinoma sensitive to oxaliplatin through the inhibition of stemness.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2011;61(2):69–90. - PubMed
-
- Ye SL, Takayama T, Geschwind J, Marrero JA, Bronowicki JP. Current approaches to the treatment of early hepatocellular carcinoma. The Oncologist. 2010;15(supplement 4):34–41. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Sala M, Llovet JM. Chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S179–S188. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine. 2011;365:1118–1127. - PubMed
-
- Carr BI. Hepatocellular carcinoma: current management and future trends. Gastroenterology. 2004;127(5, supplement 1):S218–S224. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

