TNFα levels and macrophages expression reflect an inflammatory potential of trigeminal ganglia in a mouse model of familial hemiplegic migraine
- PMID: 23326332
- PMCID: PMC3543418
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052394
TNFα levels and macrophages expression reflect an inflammatory potential of trigeminal ganglia in a mouse model of familial hemiplegic migraine
Abstract
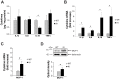
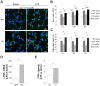
Latent changes in trigeminal ganglion structure and function resembling inflammatory conditions may predispose to acute attacks of migraine pain. Here, we investigated whether, in trigeminal sensory ganglia, cytokines such as TNFα might contribute to a local inflammatory phenotype of a transgenic knock-in (KI) mouse model of familial hemiplegic migraine type-1 (FHM-1). To this end, macrophage occurrence and cytokine expression in trigeminal ganglia were compared between wild type (WT) and R192Q mutant Ca(V)2.1 Ca(2+) channel (R192Q KI) mice, a genetic model of FHM-1. Cellular and molecular characterization was performed using a combination of confocal immunohistochemistry and cytokine assays. With respect to WT, R192Q KI trigeminal ganglia were enriched in activated macrophages as suggested by their morphology and immunoreactivity to the markers Iba1, CD11b, and ED1. R192Q KI trigeminal ganglia constitutively expressed higher mRNA levels of IL1β, IL6, IL10 and TNFα cytokines and the MCP-1 chemokine. Consistent with the report that TNFα is a major factor to sensitize trigeminal ganglia, we observed that, following an inflammatory reaction evoked by LPS injection, TNFα expression and macrophage occurrence were significantly higher in R192Q KI ganglia with respect to WT ganglia. Our data suggest that, in KI trigeminal ganglia, the complex cellular and molecular environment could support a new tissue phenotype compatible with a neuroinflammatory profile. We propose that, in FHM patients, this condition might contribute to trigeminal pain pathophysiology through release of soluble mediators, including TNFα, that may modulate the crosstalk between sensory neurons and resident glia, underlying the process of neuronal sensitisation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of LPS on P2X3 receptors of trigeminal sensory neurons and macrophages from mice expressing the R192Q Cacna1a gene mutation of familial hemiplegic migraine-1.Purinergic Signal. 2013 Mar;9(1):7-13. doi: 10.1007/s11302-012-9328-1. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Purinergic Signal. 2013. PMID: 22836594 Free PMC article.
-
Inefficient constitutive inhibition of P2X3 receptors by brain natriuretic peptide system contributes to sensitization of trigeminal sensory neurons in a genetic mouse model of familial hemiplegic migraine.Mol Pain. 2016 May 12;12:1744806916646110. doi: 10.1177/1744806916646110. Print 2016. Mol Pain. 2016. PMID: 27175010 Free PMC article.
-
Functional crosstalk in culture between macrophages and trigeminal sensory neurons of a mouse genetic model of migraine.BMC Neurosci. 2012 Nov 21;13:143. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-13-143. BMC Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23171280 Free PMC article.
-
CaV2.1 voltage activated calcium channels and synaptic transmission in familial hemiplegic migraine pathogenesis.J Physiol Paris. 2012 Jan;106(1-2):12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2011.10.004. Epub 2011 Nov 2. J Physiol Paris. 2012. PMID: 22074995 Review.
-
Calcium channels and synaptic transmission in familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 animal models.Biophys Rev. 2014 Mar;6(1):15-26. doi: 10.1007/s12551-013-0126-y. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Biophys Rev. 2014. PMID: 28509957 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Orofacial skin inflammation increases the number of macrophages in the maxillary subregion of the rat trigeminal ganglion in a corticosteroid-reversible manner.Cell Tissue Res. 2020 Dec;382(3):551-561. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03244-3. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Cell Tissue Res. 2020. PMID: 32696216 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpressed Na V 1.7 Channels Confer Hyperexcitability to in vitro Trigeminal Sensory Neurons of Ca V 2.1 Mutant Hemiplegic Migraine Mice.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 May 25;15:640709. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.640709. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34113237 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased microRNA-125a-3p contributes to upregulation of p38 MAPK in rat trigeminal ganglions with orofacial inflammatory pain.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 7;9(11):e111594. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111594. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25380251 Free PMC article.
-
Convergence of ubiquitylation and phosphorylation signaling in rapamycin-treated yeast cells.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014 Aug;13(8):1979-92. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O113.035683. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24961812 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Glia Activation by TRPA1 Antagonism in Preclinical Models of Migraine.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 15;23(22):14085. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214085. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ophoff RA, Terwindt GM, Vergouwe MN, van Eijk R, Oefner PJ, et al. (1996) Familial Hemiplegic Migraine and Episodic Ataxia Type-2 Are Caused by Mutations in the Ca2+ Channel Gene CACNL1A4. Cell 87: 543–552. - PubMed
-
- van den Maagdenberg AMJM, Haan J, Terwindt GM, Ferrari MD (2007) Migraine: gene mutations and functional consequences. Curr Opin Neurol 20: 299–305. - PubMed
-
- van den Maagdenberg AM, Pietrobon D, Pizzorusso T, Kaja S, Broos LA, et al. (2004) A Cacna1a Knockin Migraine Mouse Model with Increased Susceptibility to Cortical Spreading Depression. Neuron 41: 701–710. - PubMed
-
- Tfelt-Hansen PC, Koehler PJ (2011) One hundred years of migraine research: major clinical and scientific observations from 1910 to 2010. Headache 51, 5: 752–778. - PubMed
-
- Jurkat-Rott K, Lerche H, Weber Y, Lehmann-Horn F (2010) Hereditary channelopathies in neurology. Adv Exp Med Biol 686: 305–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

