Ginkgo biloba extract and long-term cognitive decline: a 20-year follow-up population-based study
- PMID: 23326356
- PMCID: PMC3543404
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052755
Ginkgo biloba extract and long-term cognitive decline: a 20-year follow-up population-based study
Abstract
Background: Numerous studies have looked at the potential benefits of various nootropic drugs such as Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb761®; Tanakan®) and piracetam (Nootropyl®) on age-related cognitive decline often leading to inconclusive results due to small sample sizes or insufficient follow-up duration. The present study assesses the association between intake of EGb761® and cognitive function of elderly adults over a 20-year period.
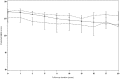
Methods and findings: The data were gathered from the prospective community-based cohort study 'Paquid'. Within the study sample of 3612 non-demented participants aged 65 and over at baseline, three groups were compared: 589 subjects reporting use of EGb761® at at least one of the ten assessment visits, 149 subjects reporting use of piracetam at one of the assessment visits and 2874 subjects not reporting use of either EGb761® or piracetam. Decline on MMSE, verbal fluency and visual memory over the 20-year follow-up was analysed with a multivariate mixed linear effects model. A significant difference in MMSE decline over the 20-year follow-up was observed in the EGb761® and piracetam treatment groups compared to the 'neither treatment' group. These effects were in opposite directions: the EGb761® group declined less rapidly than the 'neither treatment' group, whereas the piracetam group declined more rapidly (β = -0.6). Regarding verbal fluency and visual memory, no difference was observed between the EGb761® group and the 'neither treatment' group (respectively, β = 0.21 and β = -0.03), whereas the piracetam group declined more rapidly (respectively, β = -1.40 and β = -0.44). When comparing the EGb761® and piracetam groups directly, a different decline was observed for the three tests (respectively β = -1.07, β = -1.61 and β = -0.41).
Conclusion: Cognitive decline in a non-demented elderly population was lower in subjects who reported using EGb761® than in those who did not. This effect may be a specific medication effect of EGb761®, since it was not observed for another nootropic medication, piracetam.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Rockwood K, Kirkland S, Hogan DB, MacKnight C, Merry H, et al. (2002) Use of lipid-lowering agents, indication bias, and the risk of dementia in community-dwelling elderly people. Arch Neurol 59: 223–227. - PubMed
-
- Trompet S, van Vliet P, de Craen AJ, Jolles J, Buckley BM, et al. (2010) Pravastatin and cognitive function in the elderly. Results of the PROSPER study. J Neurol 257: 85–90. - PubMed
-
- van Vliet P, van de Water W, de Craen AJ, Westendorp RG (2009) The influence of age on the association between cholesterol and cognitive function. Exp Gerontol 44: 112–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

