Genetically modified α-amylase inhibitor peas are not specifically allergenic in mice
- PMID: 23326368
- PMCID: PMC3541390
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052972
Genetically modified α-amylase inhibitor peas are not specifically allergenic in mice
Abstract
Weevils can devastate food legumes in developing countries, but genetically modified peas (Pisum sativum), chickpeas and cowpeas expressing the gene for alpha-amylase inhibitor-1 (αAI) from the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) are completely protected from weevil destruction. αAI is seed-specific, accumulated at high levels and undergoes post-translational modification as it traverses the seed endomembrane system. This modification was thought to be responsible for the reported allergenicity in mice of the transgenic pea but not the bean. Here, we observed that transgenic αAI peas, chickpeas and cowpeas as well as non-transgenic beans were all allergenic in BALB/c mice. Even consuming non-transgenic peas lacking αAI led to an anti-αAI response due to a cross-reactive response to pea lectin. Our data demonstrate that αAI transgenic peas are not more allergenic than beans or non-transgenic peas in mice. This study illustrates the importance of repeat experiments in independent laboratories and the potential for unexpected cross-reactive allergic responses upon consumption of plant products in mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
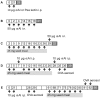
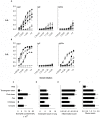
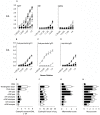
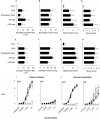
 , PBS alone ×, Tendergreen bean ▪, αAI pea ▴ and nGM pea ▵ gavaged mice. Data are expressed as mean OD450 nm ± SEM; n = 8, duplicate samples. For IgE, dilutions are expressed ×103. Data are expressed as means ± SEM; n = 8. For eosinophil counts in BAL and lungs, data were compared using the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test. For histological scoring, data were compared with the Mann Whitney test. *p<0.05 for all groups above the PBS controls. These are representative data from 2 experiments.
, PBS alone ×, Tendergreen bean ▪, αAI pea ▴ and nGM pea ▵ gavaged mice. Data are expressed as mean OD450 nm ± SEM; n = 8, duplicate samples. For IgE, dilutions are expressed ×103. Data are expressed as means ± SEM; n = 8. For eosinophil counts in BAL and lungs, data were compared using the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test. For histological scoring, data were compared with the Mann Whitney test. *p<0.05 for all groups above the PBS controls. These are representative data from 2 experiments.Similar articles
-
Comparison of the α-amylase inhibitor-1 from common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) varieties and transgenic expression in other legumes--post-translational modifications and immunogenicity.J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Jun 8;59(11):6047-54. doi: 10.1021/jf200456j. Epub 2011 May 13. J Agric Food Chem. 2011. PMID: 21542649
-
Bean alpha-amylase inhibitor 1 in transgenic peas (Pisum sativum) provides complete protection from pea weevil (Bruchus pisorum) under field conditions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Apr 11;97(8):3820-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.070054597. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10759552 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic expression of bean alpha-amylase inhibitor in peas results in altered structure and immunogenicity.J Agric Food Chem. 2005 Nov 16;53(23):9023-30. doi: 10.1021/jf050594v. J Agric Food Chem. 2005. PMID: 16277398
-
Legume Allergens Pea, Chickpea, Lentil, Lupine and Beyond.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024 Sep;24(9):527-548. doi: 10.1007/s11882-024-01165-7. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024. PMID: 38990406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Legume cross-reactivity].Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2003 May-Jun;31(3):151-61. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2003. PMID: 12783766 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
No adjuvant effect of Bacillus thuringiensis-maize on allergic responses in mice.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 1;9(8):e103979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103979. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25084284 Free PMC article.
-
Research gaps and future needs for allergen prediction in food safety.Front Allergy. 2024 Feb 19;5:1297547. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2024.1297547. eCollection 2024. Front Allergy. 2024. PMID: 38440401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Update on Genetic Modification of Chickpea for Increased Yield and Stress Tolerance.Mol Biotechnol. 2018 Aug;60(8):651-663. doi: 10.1007/s12033-018-0096-1. Mol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29946933 Review.
-
Allergic sensitization: screening methods.Clin Transl Allergy. 2014 Apr 15;4(1):13. doi: 10.1186/2045-7022-4-13. Clin Transl Allergy. 2014. PMID: 24739743 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of scientific studies usually cited as evidence of adverse effects of GM food/feed.Plant Biotechnol J. 2017 Oct;15(10):1227-1234. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12798. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Plant Biotechnol J. 2017. PMID: 28710840 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- James C (2011) Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2011. ISAAA Brief ISAAA: Ithaca, NY.
-
- Higgins T, Gollasch S, Molvig L, Moore A, Popelka C, et al... Insect-protected cowpeas using gene technology. In: Fatokun C, editor; 2012; Saly, Senegal. IITA. pp. In Press.
-
- Sarmah BK, Moore A, Tate W, Molvig L, Morton RL, et al. (2004) Transgenic chickpea seeds expressing high levels of a bean α-amylase inhibitor. Molecular Breeding 14: 73–82.
-
- Shade RE, Schroeder HE, Pueyo JJ, Tabe LM, Murdock LL, et al. (1994) Transgenic pea seeds expressing the α-amylase inhibitor of the common bean are resistant to bruchid beetles. Nat Biotech 12: 793–796.
-
- Campbell PM, Reiner D, Moore AE, Lee RY, Epstein MM, et al. (2011) Comparison of the alpha-amylase inhibitor-1 from common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) varieties and transgenic expression in other legumes–post-translational modifications and immunogenicity. J Agric Food Chem 59: 6047–6054. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

