VEGF, HIF-1α expression and MVD as an angiogenic network in familial breast cancer
- PMID: 23326384
- PMCID: PMC3543407
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053070
VEGF, HIF-1α expression and MVD as an angiogenic network in familial breast cancer
Abstract
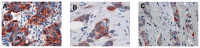
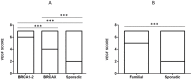
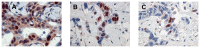
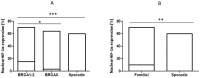
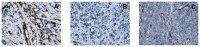
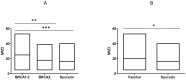
Angiogenesis, which plays an important role in tumor growth and progression of breast cancer, is regulated by a balance between pro- and anti-angiogenic factors. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is up-regulated during hypoxia by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α). It is known that there is an interaction between HIF-1α and BRCA1 carrier cancers, but little has been reported about angiogenesis in BRCA1-2 carrier and BRCAX breast cancers. In this study, we investigated the expression of VEGF and HIF-1α and microvessel density (MVD) in 26 BRCA1-2 carriers and 58 BRCAX compared to 77 sporadic breast cancers, by immunohistochemistry. VEGF expression in BRCA1-2 carriers was higher than in BRCAX cancer tissues (p = 0.0001). Furthermore, VEGF expression was higher in both BRCA1-2 carriers and BRCAX than the sporadic group (p<0.0001). VEGF immunoreactivity was correlated with poor tumor grade (p = 0.0074), hormone receptors negativity (p = 0.0206, p = 0.0002 respectively), and MIB-1-labeling index (p = 0.0044) in familial cancers (BRCA1-2 and BRCAX). The percentage of nuclear HIF-1α expression was higher in the BRCA1-2 carriers than in BRCAX cancers (p<0.05), and in all familial than in sporadic tumor tissues (p = 0.0045). A higher MVD was observed in BRCA1-2 carrier than in BRCAX and sporadic cancer tissues (p = 0.002, p = 0.0001 respectively), and in all familial tumors than in sporadic tumors (p = 0.01). MVD was positively related to HIF-1α expression in BRCA1-2 carriers (r = 0.521, p = 0.006), and, in particular, we observed a highly significant correlation in the familial group (r = 0.421, p<0.0001). Our findings suggest that angiogenesis plays a crucial role in BRCA1-2 carrier breast cancers. Prospective studies in larger BRCA1-2 carrier series are needed to improve the best therapeutic strategies for this subgroup of breast cancer patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha), and microvessel density in endometrial tissue in women with adenomyosis.Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2009 Mar;28(2):157-63. doi: 10.1097/PGP.0b013e318182c2be. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19188818
-
Hypoxia-induced factor-1 alpha, vascular endothelial growth factor expression in BRCA1-related breast cancer: A prospective study in tertiary care hospital.Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2017 Oct-Dec;60(4):469-474. doi: 10.4103/IJPM.IJPM_524_16. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29323057
-
HIF-1α overexpression in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56055. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056055. Epub 2013 Feb 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23409121 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-1α, VEGF and WT-1 are protagonists in bilateral primary angiosarcoma of breast: a case report and review of literature.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(3):247-53. Epub 2012 Mar 25. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22558480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiogenesis induction in breast cancer: A paracrine paradigm.Cell Biochem Funct. 2021 Oct;39(7):860-873. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3663. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Cell Biochem Funct. 2021. PMID: 34505714 Review.
Cited by
-
Pregnancy-specific glycoprotein 9 (PSG9), a driver for colorectal cancer, enhances angiogenesis via activation of SMAD4.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 20;7(38):61562-61574. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11146. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27528036 Free PMC article.
-
High FSH levels impair VEGF secretion of human, frozen-thawed ovarian cortical tissue in vitro.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 8;14(1):3287. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53402-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38332226 Free PMC article.
-
Histopathological growth pattern and vessel co-option in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.Med Mol Morphol. 2024 Sep;57(3):200-217. doi: 10.1007/s00795-024-00392-1. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Med Mol Morphol. 2024. PMID: 38960952 Free PMC article.
-
Possible biological and translational significance of mast cells density in colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 21;20(27):8910-20. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8910. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25083063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of BRCA1/2-Mutated Tumor Microenvironment in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 2;13(3):575. doi: 10.3390/cancers13030575. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33540843 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Autier P, Boniol M, Heanue M, Colombet M, et al. (2007) Estimates of the cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2006. Ann Oncol 18 3: 581–592 doi: mdl498 [pii] 10.1093/annonc/mdl498. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Ramires R, Gomez G, Munoz-Repeto I, de Cecco L, Llort G, et al. (2011) Transcriptional characteristics of familial non-BRCA1/BRCA2 breast tumors. Int J Cancer 128 11: 2635–2644 doi:10.1002/ijc.25603. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vargas AC, Reis-Filho JS, Lakhani SR (2011) Phenotype-genotype correlation in familial breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 16 1: 27–40 doi:10.1007/s10911-011-9204-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van der Groep P, van der Wall E, van Diest PJ (2011) Pathology of hereditary breast cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 34 2: 71–88 doi:10.1007/s13402-011-0010-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

