Histone deacetylase inhibition decreases cholesterol levels in neuronal cells by modulating key genes in cholesterol synthesis, uptake and efflux
- PMID: 23326422
- PMCID: PMC3542332
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053394
Histone deacetylase inhibition decreases cholesterol levels in neuronal cells by modulating key genes in cholesterol synthesis, uptake and efflux
Abstract
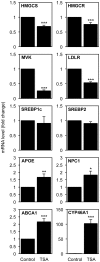
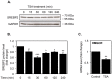
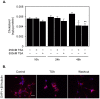
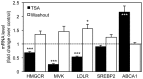
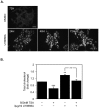
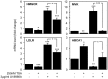
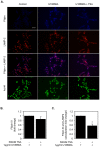
Cholesterol is an essential component of the central nervous system and increasing evidence suggests an association between brain cholesterol metabolism dysfunction and the onset of neurodegenerative disorders. Interestingly, histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) such as trichostatin A (TSA) are emerging as promising therapeutic approaches in neurodegenerative diseases, but their effect on brain cholesterol metabolism is poorly understood. We have previously demonstrated that HDACi up-regulate CYP46A1 gene transcription, a key enzyme in neuronal cholesterol homeostasis. In this study, TSA was shown to modulate the transcription of other genes involved in cholesterol metabolism in human neuroblastoma cells, namely by up-regulating genes that control cholesterol efflux and down-regulating genes involved in cholesterol synthesis and uptake, thus leading to an overall decrease in total cholesterol content. Furthermore, co-treatment with the amphipathic drug U18666A that can mimic the intracellular cholesterol accumulation observed in cells of Niemman-Pick type C patients, revealed that TSA can ameliorate the phenotype induced by pathological cholesterol accumulation, by restoring the expression of key genes involved in cholesterol synthesis, uptake and efflux and promoting lysosomal cholesterol redistribution. These results clarify the role of TSA in the modulation of neuronal cholesterol metabolism at the transcriptional level, and emphasize the idea of HDAC inhibition as a promising therapeutic tool in neurodegenerative disorders with impaired cholesterol metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Okadaic acid inhibits the trichostatin A-mediated increase of human CYP46A1 neuronal expression in a ERK1/2-Sp3-dependent pathway.J Lipid Res. 2012 Sep;53(9):1910-9. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M027680. Epub 2012 Jun 12. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22693257 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: a new mode for inhibition of cholesterol metabolism.BMC Genomics. 2008 Oct 29;9:507. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-507. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18959802 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin-modifying agents increase transcription of CYP46A1, a key player in brain cholesterol elimination.J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;22(4):1209-21. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-100651. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010. PMID: 20930312
-
Potential Use of the Cholesterol Transfer Inhibitor U18666A as a Potent Research Tool for the Study of Cholesterol Mechanisms in Neurodegenerative Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jun;61(6):3503-3527. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03798-7. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37995080 Review.
-
Cholesterol Hydroxylating Cytochrome P450 46A1: From Mechanisms of Action to Clinical Applications.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Jul 8;13:696778. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.696778. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34305573 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Altered Cholesterol Intracellular Trafficking and the Development of Pathological Hallmarks of Sporadic AD.J Parkinsons Dis Alzheimers Dis. 2014;1(1):8. doi: 10.13188/2376-922x.1000002. J Parkinsons Dis Alzheimers Dis. 2014. PMID: 25621310 Free PMC article.
-
The Antihypertensive Drug Telmisartan Protects Oligodendrocytes from Cholesterol Accumulation and Promotes Differentiation by a PPAR-γ-Mediated Mechanism.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 30;22(17):9434. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179434. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502342 Free PMC article.
-
MFN2 coordinates mitochondria motility with α-tubulin acetylation and this regulation is disrupted in CMT2A.iScience. 2024 May 15;27(6):109994. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109994. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38883841 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Effects of Known and Novel HDAC and SIRT Inhibitors in Glioblastomas Independently or Combined with Temozolomide.Metabolites. 2014 Sep 12;4(3):807-30. doi: 10.3390/metabo4030807. Metabolites. 2014. PMID: 25222834 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of cholesterol homeostasis in sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase-deficient fibroblasts reveals a Niemann-Pick disease type C-like phenotype with enhanced lysosomal Ca2+ storage.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 6;7:43575. doi: 10.1038/srep43575. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28262793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dietschy JM, Turley SD (2004) Thematic review series: brain Lipids. Cholesterol metabolism in the central nervous system during early development and in the mature animal. J Lipid Res 45: 1375–1397. - PubMed
-
- Strittmatter WJ, Roses AD (1996) Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 19: 53–77. - PubMed
-
- Zlokovic BV (2008) The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron 57: 178–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

