Immediate and heterogeneous response of the LiaFSR two-component system of Bacillus subtilis to the peptide antibiotic bacitracin
- PMID: 23326432
- PMCID: PMC3543457
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053457
Immediate and heterogeneous response of the LiaFSR two-component system of Bacillus subtilis to the peptide antibiotic bacitracin
Abstract
Background: Two-component signal transduction systems are one means of bacteria to respond to external stimuli. The LiaFSR two-component system of Bacillus subtilis consists of a regular two-component system LiaRS comprising the core Histidine Kinase (HK) LiaS and the Response Regulator (RR) LiaR and additionally the accessory protein LiaF, which acts as a negative regulator of LiaRS-dependent signal transduction. The complete LiaFSR system was shown to respond to various peptide antibiotics interfering with cell wall biosynthesis, including bacitracin.
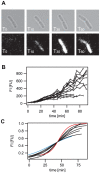
Methodology and principal findings: Here we study the response of the LiaFSR system to various concentrations of the peptide antibiotic bacitracin. Using quantitative fluorescence microscopy, we performed a whole population study analyzed on the single cell level. We investigated switching from the non-induced 'OFF' state into the bacitracin-induced 'ON' state by monitoring gene expression of a fluorescent reporter from the RR-regulated liaI promoter. We found that switching into the 'ON' state occurred within less than 20 min in a well-defined switching window, independent of the bacitracin concentration. The switching rate and the basal expression rate decreased at low bacitracin concentrations, establishing clear heterogeneity 60 min after bacitracin induction. Finally, we performed time-lapse microscopy of single cells confirming the quantitative response as obtained in the whole population analysis for high bacitracin concentrations.
Conclusion: The LiaFSR system exhibits an immediate, heterogeneous and graded response to the inducer bacitracin in the exponential growth phase.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Castelli M, Vescvi EG, Soncini FC (2000) The phosphatase activity is the target for Mg2+ regulation of the sensor protein PhoQ in Salmonella . J Biol Chem 275: 22948–22954. - PubMed
-
- Stock A, Robinson VL, Gourdreau PN (2000) Two-component signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem 69: 183–215. - PubMed
-
- Nagasawa S, Tokishita S, Aiba H, Mizuno T (1997) A novel sensor-regulator protein that belongs to the homologous family of signal transduction proteins involved in adaptive responses in Escherichia coli . DNA Res 4: 161–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

