Combination of a proteomics approach and reengineering of meso scale network models for prediction of mode-of-action for tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 23326482
- PMCID: PMC3541187
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053668
Combination of a proteomics approach and reengineering of meso scale network models for prediction of mode-of-action for tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Abstract
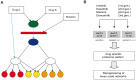
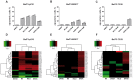
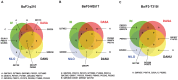
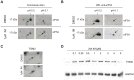
In drug discovery, the characterisation of the precise modes of action (MoA) and of unwanted off-target effects of novel molecularly targeted compounds is of highest relevance. Recent approaches for identification of MoA have employed various techniques for modeling of well defined signaling pathways including structural information, changes in phenotypic behavior of cells and gene expression patterns after drug treatment. However, efficient approaches focusing on proteome wide data for the identification of MoA including interference with mutations are underrepresented. As mutations are key drivers of drug resistance in molecularly targeted tumor therapies, efficient analysis and modeling of downstream effects of mutations on drug MoA is a key to efficient development of improved targeted anti-cancer drugs. Here we present a combination of a global proteome analysis, reengineering of network models and integration of apoptosis data used to infer the mode-of-action of various tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cell lines expressing wild type as well as TKI resistance conferring mutants of BCR-ABL. The inferred network models provide a tool to predict the main MoA of drugs as well as to grouping of drugs with known similar kinase inhibitory activity patterns in comparison to drugs with an additional MoA. We believe that our direct network reconstruction approach, demonstrated on proteomics data, can provide a complementary method to the established network reconstruction approaches for the preclinical modeling of the MoA of various types of targeted drugs in cancer treatment. Hence it may contribute to the more precise prediction of clinically relevant on- and off-target effects of TKIs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
All tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant chronic myelogenous cells are highly sensitive to ponatinib.Oncotarget. 2012 Dec;3(12):1557-65. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.692. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 23238683 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydroartemisinin inhibits the Bcr/Abl oncogene at the mRNA level in chronic myeloid leukemia sensitive or resistant to imatinib.Biomed Pharmacother. 2013 Mar;67(2):157-63. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2012.10.017. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 23201011
-
Simultaneous targeting of Aurora kinases and Bcr-Abl kinase by the small molecule inhibitor PHA-739358 is effective against imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL mutations including T315I.Blood. 2008 Apr 15;111(8):4355-64. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-113175. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18268096
-
In vitro anti-leukaemia activity of pyrrolo[1,2-b][1,2,5]benzothiadiazepines (PBTDs).Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2010 Jan;5(1):58-68. doi: 10.2174/157489210789702163. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2010. PMID: 19663771 Review.
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia: approach to patients with treatment-naive or refractory chronic-phase disease.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2011;2011:121-7. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2011.1.121. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2011. PMID: 22160023 Review.
Cited by
-
From hype to reality: data science enabling personalized medicine.BMC Med. 2018 Aug 27;16(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12916-018-1122-7. BMC Med. 2018. PMID: 30145981 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome Changes Induced by Imatinib and Novel Imatinib Derivatives in K562 Human Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells.Proteomes. 2014 Jul 22;2(3):363-381. doi: 10.3390/proteomes2030363. Proteomes. 2014. PMID: 28250386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sebolt-Leopold JS, English JM (2006) Mechanisms of drug inhibition of signalling molecules. Nature 441: 457–462. - PubMed
-
- Cohen P (2002) Protein kinases [mdash] the major drug targets of the twenty-first century? Nat Rev Drug Discov 1: 309–315. - PubMed
-
- Dancey J, Sausville EA (2003) Issues and progress with protein kinase inhibitors for cancer treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2: 296–313. - PubMed
-
- Karaman MW, Herrgard S, Treiber DK, Gallant P, Atteridge CE, et al. (2008) A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat Biotech 26: 127–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

