Effects of initial cell density and hydrodynamic culture on osteogenic activity of tissue-engineered bone grafts
- PMID: 23326488
- PMCID: PMC3543387
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053697
Effects of initial cell density and hydrodynamic culture on osteogenic activity of tissue-engineered bone grafts
Abstract
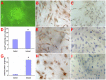
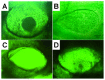
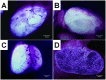
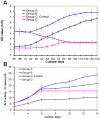
This study aimed to study the effects of initial cell density and in vitro culture method on the construction of tissue-engineered bone grafts and osteogenic activities. Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) were seeded onto cubic scaffolds prepared from demineralized bone matrix (DBM) by three methods - static, hydrodynamic, or fibrin hydrogel-assisted seeding. The resulting cell-scaffold constructs were cultured in vitro by static flask culture or hydrodynamic culture. The initial cell density and the subsequent in vitro proliferation and alkaline phosphate activities of the constructs were analyzed. The constructs were also subcutaneously implanted in nude mice to examine their in vivo osteogenic activities. Hydrogel-assisted seeding gave the highest seeding efficiency, followed by hydrodynamic and conventional static seeding. During in vitro culture, hydrodynamic culture produced higher plateau cell densities, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activities, and extracellular matrix production than static culture. After subcutaneous implantation in nude mice, the implants prepared by the combination of hydrogel-assisted seeding and hydrodynamic culture produced higher wet weight and bone mineral density than implants prepared by other methods. The results suggest that the hydrogel-assisted seeding can substantially increase the initial seed cell density in scaffolds. Subsequent hydrodynamic culture can promote the proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation of the seeded cells. Correspondingly, bone grafts produced by the combination of these two methods achieved the highest osteogenic activity among the three methods employed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
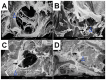
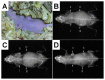
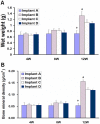
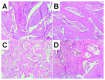
References
-
- Ouyang A, Yang ST (2007) Effects of mixing intensity on cell seeding and proliferation in three-dimensional fibrous matrices. Biotechnol Bioeng 96: 371–380. - PubMed
-
- Zhang ZY, Teoh SH, Chong WS, Foo TT, Chng YC, et al. (2009) A biaxial rotating bioreactor for the culture of fetal mesenchymal stem cells for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 30: 2694–2704. - PubMed
-
- Seebach C, Schultheiss J, Wilhelm K, Frank J, Henrich D (2010) Comparison of six bone-graft substitutes regarding to cell seeding efficiency, metabolism and growth behaviour of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in vitro. Injury 41: 731–738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

