Mediator subunit18 controls flowering time and floral organ identity in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 23326539
- PMCID: PMC3543355
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053924
Mediator subunit18 controls flowering time and floral organ identity in Arabidopsis
Abstract
Mediator is a conserved multi-protein complex that plays an important role in regulating transcription by mediating interactions between transcriptional activator proteins and RNA polymerase II. Much evidence exists that Mediator plays a constitutive role in the transcription of all genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II. However, evidence is mounting that specific Mediator subunits may control the developmental regulation of specific subsets of RNA polymerase II-dependent genes. Although the Mediator complex has been extensively studied in yeast and mammals, only a few reports on Mediator function in flowering time control of plants, little is known about Mediator function in floral organ identity. Here we show that in Arabidopsis thaliana, MEDIATOR SUBUNIT 18 (MED18) affects flowering time and floral organ formation through FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC) and AGAMOUS (AG). A MED18 loss-of-function mutant showed a remarkable syndrome of later flowering and altered floral organ number. We show that FLC and AG mRNA levels and AG expression patterns are altered in the mutant. Our results support parallels between the regulation of FLC and AG and demonstrate a developmental role for Mediator in plants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

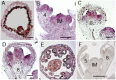
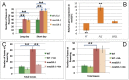
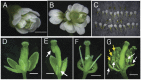
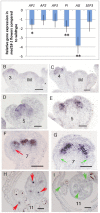
References
-
- Blazek E, Mittler G, Meisterernst M (2005) The mediator of RNA polymerase II. Chromosoma 113: 399–408. - PubMed
-
- Casamassimi A, Napoli C (2007) Mediator complexes and eukaryotic transcription regulation: an overview. Biochimie 89: 1439–1446. - PubMed
-
- Kornberg RD (2005) Mediator and the mechanism of transcriptional activation. Trends Biochem Sci 30: 235–239. - PubMed
-
- Backstrom S, Elfving N, Nilsson R, Wingsle G, Bjorklund S (2007) Purification of a plant mediator from Arabidopsis thaliana identifies PFT1 as the Med25 subunit. Mol Cell 26: 717–729. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

