Predictive modeling using a somatic mutational profile in ovarian high grade serous carcinoma
- PMID: 23326577
- PMCID: PMC3542368
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054089
Predictive modeling using a somatic mutational profile in ovarian high grade serous carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Recent high-throughput sequencing technology has identified numerous somatic mutations across the whole exome in a variety of cancers. In this study, we generate a predictive model employing the whole exome somatic mutational profile of ovarian high-grade serous carcinomas (Ov-HGSCs) obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas data portal.
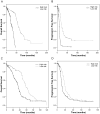
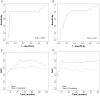
Methods: A total of 311 patients were included for modeling overall survival (OS) and 259 patients were included for modeling progression free survival (PFS) in an analysis of 509 genes. The model was validated with complete leave-one-out cross-validation involving re-selecting genes for each iteration of the cross-validation procedure. Cross-validated Kaplan-Meier curves were generated. Cross-validated time dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were computed and the area under the curve (AUC) values were calculated from the ROC curves to estimate the predictive accuracy of the survival risk models.
Results: There was a significant difference in OS between the high-risk group (median, 28.1 months) and the low-risk group (median, 61.5 months) (permutated p-value <0.001). For PFS, there was also a significant difference in PFS between the high-risk group (10.9 months) and the low-risk group (22.3 months) (permutated p-value <0.001). Cross-validated AUC values were 0.807 for the OS and 0.747 for the PFS based on a defined landmark time t = 36 months. In comparisons between a predictive model containing only gene variables and a combined model containing both gene variables and clinical covariates, the predictive model containing gene variables without clinical covariates were effective and high AUC values for both OS and PFS were observed.
Conclusions: We designed a predictive model using a somatic mutation profile obtained from high-throughput genomic sequencing data in Ov-HGSC samples that may represent a new strategy for applying high-throughput sequencing data to clinical practice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Simon R, Radmacher MD, Dobbin K, McShane LM (2003) Pitfalls in the use of DNA microarray data for diagnostic and prognostic classification. J Natl Cancer Inst 95: 14–18. - PubMed
-
- Molinaro AM, Simon R, Pfeiffer RM (2005) Prediction error estimation: a comparison of resampling methods. Bioinformatics 21: 3301–3307. - PubMed
-
- Moynahan ME, Pierce AJ, Jasin M (2001) BRCA2 is required for homology-directed repair of chromosomal breaks. Mol Cell 7: 263–272. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

