Functional mapping of protein kinase A reveals its importance in adult Schistosoma mansoni motor activity
- PMID: 23326613
- PMCID: PMC3542114
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001988
Functional mapping of protein kinase A reveals its importance in adult Schistosoma mansoni motor activity
Abstract
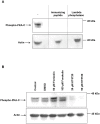
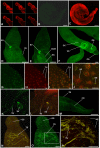
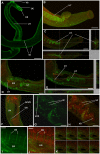
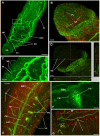
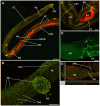
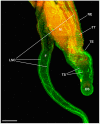
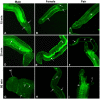
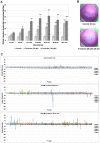
Cyclic AMP (cAMP)-dependent protein kinase/protein kinase A (PKA) is the major transducer of cAMP signalling in eukaryotic cells. Here, using laser scanning confocal microscopy and 'smart' anti-phospho PKA antibodies that exclusively detect activated PKA, we provide a detailed in situ analysis of PKA signalling in intact adult Schistosoma mansoni, a causative agent of debilitating human intestinal schistosomiasis. In both adult male and female worms, activated PKA was consistently found associated with the tegument, oral and ventral suckers, oesophagus and somatic musculature. In addition, the seminal vesicle and gynaecophoric canal muscles of the male displayed activated PKA whereas in female worms activated PKA localized to the ootype wall, the ovary, and the uterus particularly around eggs during expulsion. Exposure of live worms to the PKA activator forskolin (50 µM) resulted in striking PKA activation in the central and peripheral nervous system including at nerve endings at/near the tegument surface. Such neuronal PKA activation was also observed without forskolin treatment, but only in a single batch of worms. In addition, PKA activation within the central and peripheral nervous systems visibly increased within 15 min of worm-pair separation when compared to that observed in closely coupled worm pairs. Finally, exposure of adult worms to forskolin induced hyperkinesias in a time and dose dependent manner with 100 µM forskolin significantly increasing the frequency of gross worm movements to 5.3 times that of control worms (P≤0.001). Collectively these data are consistent with PKA playing a central part in motor activity and neuronal communication, and possibly interplay between these two systems in S. mansoni. This study, the first to localize a protein kinase when exclusively in an activated state in adult S. mansoni, provides valuable insight into the intricacies of functional protein kinase signalling in the context of whole schistosome physiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase A signalling in Schistosoma mansoni cercariae and schistosomules.Int J Parasitol. 2016 Jun;46(7):425-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2015.12.001. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Int J Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 26777870
-
Protein kinase C and extracellular signal-regulated kinase regulate movement, attachment, pairing and egg release in Schistosoma mansoni.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Jun 12;8(6):e2924. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002924. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 24921927 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental regulation of protein kinase A expression and activity in Schistosoma mansoni.Int J Parasitol. 2010 Jul;40(8):929-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Jan 22. Int J Parasitol. 2010. PMID: 20097200 Free PMC article.
-
Dual targeting of insulin and venus kinase Receptors of Schistosoma mansoni for novel anti-schistosome therapy.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013 May 16;7(5):e2226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002226. Print 2013. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013. PMID: 23696913 Free PMC article.
-
Do schistosomes grow old? A confocal laser scanning microscopy study.J Helminthol. 2010 Sep;84(3):305-11. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X0999068X. Epub 2009 Nov 27. J Helminthol. 2010. PMID: 19941681
Cited by
-
Deep phosphoproteome analysis of Schistosoma mansoni leads development of a kinomic array that highlights sex-biased differences in adult worm protein phosphorylation.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Mar 23;14(3):e0008115. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008115. eCollection 2020 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32203512 Free PMC article.
-
Computationally-guided drug repurposing enables the discovery of kinase targets and inhibitors as new schistosomicidal agents.PLoS Comput Biol. 2018 Oct 22;14(10):e1006515. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006515. eCollection 2018 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2018. PMID: 30346968 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose Uptake in the Human Pathogen Schistosoma mansoni Is Regulated Through Akt/Protein Kinase B Signaling.J Infect Dis. 2018 Jun 5;218(1):152-164. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix654. J Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29309602 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory Protein Kinase Signaling in Schistosoma mansoni Cercariae: Host Location and Invasion.J Infect Dis. 2015 Dec 1;212(11):1787-97. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv464. Epub 2015 Sep 23. J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26401028 Free PMC article.
-
Serum albumin and α-1 acid glycoprotein impede the killing of Schistosoma mansoni by the tyrosine kinase inhibitor Imatinib.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2014 Aug 7;4(3):287-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2014.07.005. eCollection 2014 Dec. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2014. PMID: 25516839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steinmann P, Keiser J, Bos R, Tanner M, Utzinger J (2006) Schistosomiasis and water resources development: systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect Dis 6: 411–425. - PubMed
-
- Popiel I, Basch PF (1984) Reproductive development of female Schistosoma mansoni (Digenia: Schistosomatidae) following bisexual pairing of worms and worm segments. J Exp Zool 232: 141–150. - PubMed
-
- Kuntz W (2001) Schistosome male-female interaction: induction of germ-cell differentiation. Trends Parasitol 17: 227–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

