What is the survival after surgery for localized malignant pleural mesothelioma?
- PMID: 23328002
- PMCID: PMC3598041
- DOI: 10.1093/icvts/ivs542
What is the survival after surgery for localized malignant pleural mesothelioma?
Abstract
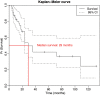
A best evidence topic in thoracic surgery was written according to a structured protocol. This was with the purpose of assisting our management of patients with localized malignant mesothelioma of the pleura (LMM). Although the terminology is used inconsistently, this variant has been formally defined by the WHO as a distinct entity defined as localized disease histologically identical to the diffuse form but without any evidence of pleural spread. Treatments for LMM include different combinations of surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. There is an impression that LMM may have a better outcome than the commoner diffuse form of malignant mesothelioma that has been reported to have a survival between 8 and 14 months. In order to advise our patients on prognosis, we studied the duration of survival after surgical resection of LMM. A total of 150 papers were found, of which 16 represented the best evidence to answer the question. The authors, journal, date, country of publication, study type, relevant outcomes and results of these papers are tabulated. It is difficult to combine the results of these 16 papers because both treatments and results are reported differently. Some report median survival (range: 11.6-36 months) and others disease-free survival (range: 0 months to 11 years). Median survival to the longest follow-up was 29 months when calculated by pooling data from informative papers using the Kaplan-Meier method. Our review suggests that survival in LMM is longer than that generally quoted for the more common diffuse form of malignant mesothelioma. Hence, aggressive treatment of LMM may be reasonable in appropriate patients.
Figures
References
-
- Churg A, Roggli V, Galateau-Salle F, Roggli PHT, Gibbs AR, Haselton PHS, et al. Pathology and Genetics. Tumors of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus, and Heart World Health Organization. Lyon. France: IARC; 2004. Tumor of the pleura. Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Hermelink HK, Harris CC (eds) pp. 128–44.
-
- Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A, editors. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th edn. New York, NY: Springer; 2010. Pleural mesothelioma; pp. 271–7.
-
- Allen TC, Cagle PT, Churg AM, Colby T, Gibbs A, Hammar S, et al. Localized malignant mesothelioma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29:866–73. doi:10.1097/01.pas.0000165529.78945.dc. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Robinson LA, Reilly RB. Localized pleural mesothelioma. The clinical spectrum. Chest. 1994;106:1611–5. - PubMed
-
- Steele J. Prognostic factors for mesothelioma. Hematol Oncol Clin N Am. 2005;19:1041–52. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2005.09.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical