Keratinocyte growth factor-2 stimulates P-glycoprotein expression and function in intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 23328208
- PMCID: PMC3602685
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00445.2012
Keratinocyte growth factor-2 stimulates P-glycoprotein expression and function in intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
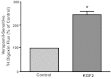
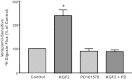
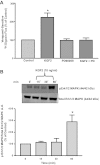
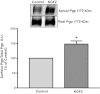
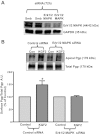
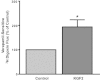
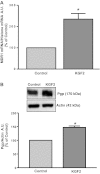
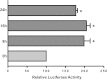
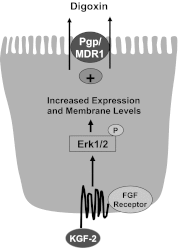
Intestinal P-glycoprotein (Pgp/multidrug resistance 1), encoded by the ATP-binding cassette B1 gene, is primarily involved in the transepithelial efflux of toxic metabolites and xenobiotics from the mucosa into the gut lumen. Reduced Pgp function and expression has been shown to be associated with intestinal inflammatory disorders. Keratinocyte growth factor-2 (KGF2) has emerged as a potential target for modulation of intestinal inflammation and maintenance of gut mucosal integrity. Whether KGF2 directly regulates Pgp in the human intestine is not known. Therefore, the present studies were undertaken to determine the modulation of Pgp by KGF2 using Caco-2 cells. Short-term treatment of Caco-2 cells with KGF2 (10 ng/ml, 1 h) increased Pgp activity (~2-fold, P < 0.05) as measured by verapamil-sensitive [(3)H]digoxin flux. This increase in Pgp function was associated with an increase in surface Pgp levels. The specific fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) antagonist PD-161570 blocked the KGF2-mediated increase in Pgp activity. Inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway by PD-98059 attenuated the stimulatory effects of KGF2 on Pgp activity. Small-interfering RNA knockdown of Erk1/2 MAPK blocked the increase in surface Pgp levels by KGF2. Long-term treatment with KGF2 (10 ng/ml, 24 h) also significantly increased PgP activity, mRNA, protein expression, and promoter activity. The long-term effects of KGF2 on Pgp promoter activity were also blocked by the FGFR antagonist and mediated by the Erk1/2 MAPK pathway. In conclusion, our findings define the posttranslational and transcriptional mechanisms underlying stimulation of Pgp function and expression by KGF2 that may contribute to the beneficial effects of KGF2 in intestinal inflammatory disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Asaki T, Konishi M, Miyake A, Kato S, Tomizawa M, Itoh N. Roles of fibroblast growth factor 10 (Fgf10) in adipogenesis in vivo. Mol Cell Endocrinol 218: 119–128, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Avissar NE, Sax HC, Toia L. In human entrocytes, GLN transport and ASCT2 surface expression induced by short-term EGF are MAPK, PI3K, and Rho-dependent. Dig Dis Sci 53: 2113–2125, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Blaisdell CJ, Pellettieri JP, Loughlin CE, Chu S, Zeitlin PL. Keratinocyte growth factor stimulates CLC-2 expression in primary fetal rat distal lung epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 20: 842–847, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Blokzijl H, Vander Borght S, Bok LI, Libbrecht L, Geuken M, van den Heuvel FA, Dijkstra G, Roskams TA, Moshage H, Jansen PL, Faber KN. Decreased P-glycoprotein (P-gp/MDR1) expression in inflamed human intestinal epithelium is independent of PXR protein levels. Inflamm Bowel Dis 13: 710–720, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK071596/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK096254/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-81858/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- IK6 BX005243/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- DK-71596/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK092441/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-96254/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-92441/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-74458/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054016/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK-67887/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-54016/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000152/BX/BLRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

