Regression of glioma tumor growth in F98 and U87 rat glioma models by the Nitrone OKN-007
- PMID: 23328810
- PMCID: PMC3578492
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nos337
Regression of glioma tumor growth in F98 and U87 rat glioma models by the Nitrone OKN-007
Abstract
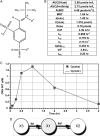
Background: Glioblastoma multiforme, a World Health Organization grade IV glioma, has a poor prognosis in humans despite current treatment options. Here, we present magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data regarding the regression of aggressive rat F98 gliomas and human U87 glioma xenografts after treatment with the nitrone compound OKN-007, a disulfonyl derivative of α-phenyl-tert-butyl nitrone.
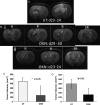
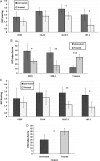
Methods: MRI was used to assess tumor volumes in F98 and U87 gliomas, and bioluminescence imaging was used to measure tumor volumes in F98 gliomas encoded with the luciferase gene (F98(luc)). Immunohistochemistry was used to assess angiogenesis (vascular endothelial growth factor [VEGF] and microvessel density [MVD]), cell differentiation (carbonic anhydrase IX [CA-IX]), hypoxia (hypoxia-inducible factor-1α [HIF-1α]), cell proliferation (glucose transporter 1 [Glut-1] and MIB-1), proliferation index, and apoptosis (cleaved caspase 3) markers in F98 gliomas. VEGF, CA-IX, Glut-1, HIF-1α, and cleaved caspase 3 were assessed in U87 gliomas.
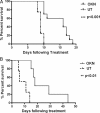
Results: Animal survival was found to be significantly increased (P < .001 for F98, P < .01 for U87) in the group that received OKN-007 treatment compared with the untreated groups. After MRI detection of F98 gliomas, OKN-007, administered orally, was found to decrease tumor growth (P < .05). U87 glioma volumes were found to significantly decrease (P < .05) after OKN-007 treatment, compared with untreated animals. OKN-007 administration resulted in significant decreases in tumor hypoxia (HIF-1α [P < .05] in both F98 and U87), angiogenesis (MVD [P < .05], but not VEGF, in F98 or U87), and cell proliferation (Glut-1 [P < .05 in F98, P < .01 in U87] and MIB-1 [P < .01] in F98) and caused a significant increase in apoptosis (cleaved caspase 3 [P < .001 in F98, P < .05 in U87]), compared with untreated animals.
Conclusions: OKN-007 may be considered as a promising therapeutic addition or alternative for the treatment of aggressive human gliomas.
Figures


Similar articles
-
OKN-007 decreases tumor necrosis and tumor cell proliferation and increases apoptosis in a preclinical F98 rat glioma model.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015 Dec;42(6):1582-91. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24935. Epub 2015 Apr 29. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25920494 Free PMC article.
-
OKN-007 decreases free radical levels in a preclinical F98 rat glioma model.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Oct;87:157-68. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.026. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26119786 Free PMC article.
-
RNA interference targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1α via a novel multifunctional surfactant attenuates glioma growth in an intracranial mouse model.J Neurosurg. 2015 Feb;122(2):331-41. doi: 10.3171/2014.10.JNS132363. Epub 2014 Nov 28. J Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 25423275
-
Targeting nitric oxide and NMDA receptor-associated pathways in treatment of high grade glial tumors. Hypotheses for nitro-memantine and nitrones.Nitric Oxide. 2018 Sep 1;79:68-83. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Nitric Oxide. 2018. PMID: 29030124 Review.
-
Angiogenesis in gliomas: biology and molecular pathophysiology.Brain Pathol. 2005 Oct;15(4):297-310. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2005.tb00115.x. Brain Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16389942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Motif mimetic of epsin perturbs tumor growth and metastasis.J Clin Invest. 2015 Dec;125(12):4349-64. doi: 10.1172/JCI80349. Epub 2015 Nov 16. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 26571402 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of 188Re-labeled PEGylated nanoliposome as a radionuclide therapeutic agent in an orthotopic glioma-bearing rat model.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Jan 9;10:463-73. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S75955. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 25624760 Free PMC article.
-
OKN-007 decreases tumor necrosis and tumor cell proliferation and increases apoptosis in a preclinical F98 rat glioma model.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015 Dec;42(6):1582-91. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24935. Epub 2015 Apr 29. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25920494 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of HIF-1α in Radiosensitivity and Radiation-Induced Bystander Effects Under Hypoxia.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 25;9:637454. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.637454. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869184 Free PMC article.
-
Toca 511 plus 5-fluorocytosine in combination with lomustine shows chemotoxic and immunotherapeutic activity with no additive toxicity in rodent glioblastoma models.Neuro Oncol. 2016 Oct;18(10):1390-401. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/now089. Epub 2016 May 10. Neuro Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27166379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Central Brain Tumor Registry of the United States (CBTRUS) 2011 CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2004–2007. 2011.
-
- Niclou SP, Fack F, Rajcevic U. Glioma proteomics: status and perspectives. J Proteomics. 2010;73(10):1823–1838. - PubMed
-
- Quick A, Patel D, Hadziahmetovic M, Chakravarti A, Mehta M. Current therapeutic paradigms in glioblastoma. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2010;5(1):14–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

