Fetal growth restriction and pulmonary hypertension in premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- PMID: 23328924
- PMCID: PMC3633609
- DOI: 10.1038/jp.2012.164
Fetal growth restriction and pulmonary hypertension in premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Abstract
Objective: To identify the association between birth weight (BW)-for-gestational age (GA) and pulmonary hypertension (PHTN) at 36 weeks in infants with moderate-severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD).
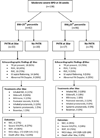
Study design: In this retrospective cohort study, we followed 138 premature infants (≤ 28 weeks) with moderate and severe BPD (National Institutes of Health consensus definition) born at Prentice Women's Hospital between 2005 and 2009. BW percentiles were calculated using the Fenton growth curve for premature infants. PHTN was determined using a standardized algorithm of echocardiogram review at 36 weeks. Logistic regression was used to evaluate the associations between BW percentile subgroups and PHTN, taking into account antenatal and neonatal factors that were related to PHTN.
Result: PHTN was associated with small BW-for-GA, ranging from thresholds of <10th to <25th percentile (P<0.001). These associations remained significant when comparing BW <25th percentile to the reference group (50 to 89 th percentile); after adjustment for GA, gender, multiple gestation, race/ethnicity (odds ratio (OR)=4.2; 95% confidence interval (CI)=1.5, 12.1); and after further adjustment for maternal vascular disease, intrauterine infection, oligohydramnios and relevant postnatal factors (OR=5.7; 95% CI=1.5, 21.2). Longitudinal follow-up of this cohort showed a trend toward higher morbidity and death among PHTN infants with BW <25th percentile.
Conclusion: BW-for-GA is an important predictor of PHTN in premature infants with moderate-severe BPD. Our findings contribute to the growing evidence supporting fetal mechanisms of later onset pulmonary vascular disease.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest or competing interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Khemani E, McElhinney DB, Rhein L, Andrade O, Lacro RV, Thomas KC, et al. Pulmonary artery hypertension in formerly premature infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical features and outcomes in the surfactant era. Pediatrics. 2007;120(6):1260–1269. - PubMed
-
- Slaughter JL, Pakrashi T, Jones DE, South AP, Shah TA. Echocardiographic detection of pulmonary hypertension in extremely low birth weight infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia requiring prolonged positive pressure ventilation. J Perinatol. 2011;31(10):635–640. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical