Germline mutations of regulator of telomere elongation helicase 1, RTEL1, in Dyskeratosis congenita
- PMID: 23329068
- PMCID: PMC3600110
- DOI: 10.1007/s00439-013-1265-8
Germline mutations of regulator of telomere elongation helicase 1, RTEL1, in Dyskeratosis congenita
Abstract
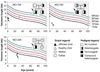
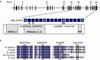
Dyskeratosis congenita (DC) is an inherited bone marrow failure and cancer predisposition syndrome caused by aberrant telomere biology. The classic triad of dysplastic nails, abnormal skin pigmentation, and oral leukoplakia is diagnostic of DC, but substantial clinical heterogeneity exists; the clinically severe variant Hoyeraal Hreidarsson syndrome (HH) also includes cerebellar hypoplasia, severe immunodeficiency, enteropathy, and intrauterine growth retardation. Germline mutations in telomere biology genes account for approximately one-half of known DC families. Using exome sequencing, we identified mutations in RTEL1, a helicase with critical telomeric functions, in two families with HH. In the first family, two siblings with HH and very short telomeres inherited a premature stop codon from their mother who has short telomeres. The proband from the second family has HH and inherited a premature stop codon in RTEL1 from his father and a missense mutation from his mother, who also has short telomeres. In addition, inheritance of only the missense mutation led to very short telomeres in the proband's brother. Targeted sequencing identified a different RTEL1 missense mutation in one additional DC proband who has bone marrow failure and short telomeres. Both missense mutations affect the helicase domain of RTEL1, and three in silico prediction algorithms suggest that they are likely deleterious. The nonsense mutations both cause truncation of the RTEL1 protein, resulting in loss of the PIP box; this may abrogate an important protein-protein interaction. These findings implicate a new telomere biology gene, RTEL1, in the etiology of DC.
Figures
Comment in
-
Telomere shortening by mutations in the RTEL1 helicase cause severe form of dyskeratosis congenita, Hoyerall-Hreidarsson syndrome.Clin Genet. 2013 Sep;84(3):210. doi: 10.1111/cge.12175. Epub 2013 May 27. Clin Genet. 2013. PMID: 23621889 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

