Gene transfer of apolipoprotein A-V improves the hypertriglyceridemic phenotype of apoa5 (-/-) mice
- PMID: 23329134
- PMCID: PMC3658105
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.301078
Gene transfer of apolipoprotein A-V improves the hypertriglyceridemic phenotype of apoa5 (-/-) mice
Abstract
Objective: Apolipoprotein (apo) A-V is a low abundance protein with a profound influence on plasma triacylglycerol levels. In human populations, single nucleotide polymorphisms and mutations in APOA5 positively correlate with hypertriglyceridemia. As an approach to preventing the deleterious effects of chronic hypertriglyceridemia, apoA-V gene therapy has been pursued.
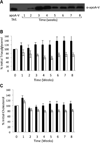
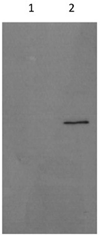
Methods and results: Recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) 2/8 harboring the coding sequence for human apoA-V or a control AAV2/8 was transduced into hypertriglyceridemic apoa5 (-/-) mice. After injection of 1×10(12) viral genome AAV2/8-apoA-V, maximal plasma levels of apoA-V protein were achieved at 3 to 4 weeks, after which the concentration slowly declined. Complementing the appearance of apoA-V was a decrease (50±6%) in plasma triacylglycerol content compared with apoa5 (-/-) mice treated with AAV2/8-β-galactosidase. After 8 weeks the mice were euthanized and plasma lipoproteins separated. AAV2/8-apoA-V-transduced mice displayed a dramatic reduction in very low-density lipoprotein triacylglycerol content. Vector generated apoA-V in plasma associated with both very low-density lipoprotein and high-density lipoprotein fractions.
Conclusions: Taken together, the data show that gene transfer of apoA-V improves the severe hypertriglyceridemia phenotype of apoa5 (-/-) mice. Given the prevalence of hypertriglyceridemia, apoA-V gene therapy offers a potential strategy for maintenance of plasma triacylglycerol homeostasis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Aberrant hetero-disulfide bond formation by the hypertriglyceridemia-associated p.Gly185Cys APOA5 variant (rs2075291).Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Oct;34(10):2254-60. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304027. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 25127531 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous injection of apolipoprotein A-V reconstituted high-density lipoprotein decreases hypertriglyceridemia in apoav-/- mice and requires glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high-density lipoprotein-binding protein 1.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010 Dec;30(12):2504-9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.210815. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20966404 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein A-V N-terminal domain lipid interaction properties in vitro explain the hypertriglyceridemic phenotype associated with natural truncation mutants.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 27;284(48):33369-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.040972. Epub 2009 Oct 13. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19825998 Free PMC article.
-
Is apolipoprotein A5 a novel regulator of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins?Ann Med. 2006;38(1):2-10. doi: 10.1080/07853890500407488. Ann Med. 2006. PMID: 16448983 Review.
-
Apoprotein A-V: an important regulator of triglyceride metabolism.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2008 Apr;31(2):281-8. doi: 10.1007/s10545-008-0863-4. Epub 2008 Apr 14. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2008. PMID: 18415697 Review.
Cited by
-
AAV-mediated gene therapy for atherosclerosis.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2014 Sep;16(9):434. doi: 10.1007/s11883-014-0434-0. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2014. PMID: 25085755 Review.
-
Biochemical and Physiological Improvement in a Mouse Model of Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome (SLOS) Following Gene Transfer with AAV Vectors.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2014;1:103-113. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2014.02.002. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2014. PMID: 25024934 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of Lipoprotein Lipase Regulation in Atherosclerosis.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 6;9(7):782. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070782. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34356847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant hetero-disulfide bond formation by the hypertriglyceridemia-associated p.Gly185Cys APOA5 variant (rs2075291).Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Oct;34(10):2254-60. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.304027. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 25127531 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of ApoA5 aggravates spontaneous and diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by reducing hepatic NR1D1 in hamsters.Theranostics. 2024 Feb 24;14(5):2036-2057. doi: 10.7150/thno.91084. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38505614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pennacchio LA, Olivier M, Hubacek JA, Cohen JC, Cox DR, Fruchart JC, Krauss RM, Rubin EM. An apolipoprotein influencing triglycerides in humans and mice revealed by comparative sequencing. Science. 2001;294:169–173. - PubMed
-
- van der Vliet HN, Sammels MG, Leegwater AC, Levels JH, Reitsma PH, Boers W, Chamuleau RA. Apolipoprotein A-V: a novel apolipoprotein associated with an early phase of liver regeneration. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:44512–44520. - PubMed
-
- Nilsson SK, Heeren J, Olivecrona G, Merkel M. Apolipoprotein A-V; a potent triglyceride reducer. Atherosclerosis. 2011;219:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Pennacchio LA, Olivier M, Hubacek JA, Krauss RM, Rubin EM, Cohen JC. Two independent apolipoprotein A5 haplotypes influence human plasma triglyceride levels. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:3031–3038. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

