Differential effect of adjuvant taxane-based and taxane-free chemotherapy regimens on the CK-19 mRNA-positive circulating tumour cells in patients with early breast cancer
- PMID: 23329233
- PMCID: PMC3593552
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.597
Differential effect of adjuvant taxane-based and taxane-free chemotherapy regimens on the CK-19 mRNA-positive circulating tumour cells in patients with early breast cancer
Abstract
Background: To determine the effect of adjuvant taxane-free and taxane-based chemotherapy regimens on the elimination of circulating tumour cells (CTCs) in patients with early breast cancer.
Methods: The presence of CK-19 mRNA-positive CTCs in the peripheral blood was evaluated before and after chemotherapy, using a real-time RT-PCR assay, in a historical comparison of two cohorts of women with stage I-III breast cancer treated with adjuvant taxane-free (N=211; FE(75)C or E(75)C) and taxane-based (N=334; T/E(75)C or T/E(75)) chemotherapy.
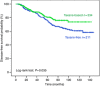
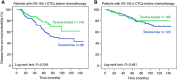
Results: Taxane-based chemotherapy resulted in a higher incidence of CTCs' elimination than taxane-free regimens since 49.7% (74 of 149) and 33.0% (29 of 88) of patients with detectable CTCs before chemotherapy, respectively, turned negative post-chemotherapy (P=0.015). Patients treated with taxane-free regimens had a significantly lower disease-free survival (DFS) (P=0.035) than patients treated with taxane-based regimens; this difference was observed in patients with but not without detectable CTCs before chemotherapy (P=0.018 and P=0.481, respectively). The incidence of deaths was significantly higher in the taxane-free cohort of patients with but not without detectable CTCs before chemotherapy compared with that of the taxane-based cohort (P=0.002). Multivariate analysis revealed that the chemotherapy regimen was significantly associated with prolonged DFS (HR: 2.00; 95% CI=1.20-3.34).
Conclusion: Elimination of CK-19 mRNA-positive CTCs during adjuvant chemotherapy seems to be an efficacy indicator of treatment and is associated with a favourable clinical outcome of patients with detectable CTCs before chemotherapy.
Figures
Comment in
-
Breast cancer: Circulating tumour cells help to guide treatment.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013 Mar;10(3):124. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.18. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23381006 No abstract available.
References
-
- Apostolaki S, Perraki M, Kallergi G, Kafousi M, Papadopoulos S, Kotsakis A, Pallis A, Xenidis N, Kalmanti L, Kalbakis K, Agelaki S, Kalykaki A, Stournaras C, Stathopoulos E, Georgoulias V, Mavroudis D. Detection of occult HER2 mRNA-positive tumor cells in the peripheral blood of patients with operable breast cancer: evaluation of their prognostic relevance. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;117 (3:525–534. - PubMed
-
- Bidard FC, Mathiot C, Delaloge S, Brain E, Giachetti S, de CP, Marty M, Pierga JY. Single circulating tumor cell detection and overall survival in nonmetastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2010;21 (4:729–733. - PubMed
-
- Bozionellou V, Mavroudis D, Perraki M, Papadopoulos S, Apostolaki S, Stathopoulos E, Stathopoulou A, Lianidou E, Georgoulias V. Trastuzumab administration can effectively target chemotherapy-resistant cytokeratin-19 messenger RNA-positive tumor cells in the peripheral blood and bone marrow of patients with breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10 (24:8185–8194. - PubMed
-
- Braun S, Vogl FD, Naume B, Janni W, Osborne MP, Coombes RC, Schlimok G, Diel IJ, Gerber B, Gebauer G, Pierga JY, Marth C, Oruzio D, Wiedswang G, Solomayer EF, Kundt G, Strobl B, Fehm T, Wong GY, Bliss J, Vincent-Salomon A, Pantel K. A pooled analysis of bone marrow micrometastasis in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353 (8:793–802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials