Orthotopic pleural mesothelioma in mice: SPECT/CT and MR imaging with HER1- and HER2-targeted radiolabeled antibodies
- PMID: 23329660
- PMCID: PMC3606545
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.12121021
Orthotopic pleural mesothelioma in mice: SPECT/CT and MR imaging with HER1- and HER2-targeted radiolabeled antibodies
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the potential of anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER)1- and anti-HER2-targeted radiolabeled antibodies and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging for imaging of orthotopic malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) in mouse models.
Materials and methods: Animal studies with 165 mice were performed in accordance with National Institutes of Health guidelines for the humane use of animals, and all procedures were approved by the institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Flow cytometry studies were performed to evaluate HER1 and HER2 expression in NCI-H226 and MSTO-211H mesothelioma cells. Biodistribution and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)/computed tomography (CT) imaging studies were performed in mice (four or five per group, depending on tumor growth) bearing subcutaneous and orthotopic MPM tumors by using HER1- and HER2-targeted indium 111 ((111)In)- and iodine 125 ((125)I)-labeled panitumumab and trastuzumab, respectively. Longitudinal MR imaging over 5 weeks was performed in three mice bearing orthotopic tumors to monitor tumor growth and metastases. SPECT/CT/MR imaging studies were performed at the final time point in the orthotopic models (n = 3). The standard unpaired Student t test was used to compare groups.
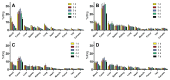
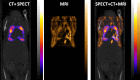
Results: Orthotopic tumors and pleural effusions were clearly visualized at MR imaging 3 weeks after tumor cell inoculation. At 2 days after injection, the mean (111)In-panitumumab uptake of 29.6% injected dose (ID) per gram ± 2.2 (standard error of the mean) was significantly greater than the (111)In-trastuzumab uptake of 13.6% ID/g ± 1.0 and the (125)I-panitumumab uptake of 7.4% ID/g ± 1.2 (P = .0006 and P = .0001, respectively). MR imaging fusion with SPECT/CT provided more accurate information about (111)In-panitumumab localization in the tumor, as the tumor was poorly visualized at CT alone.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the utility of radiolabeled anti-HER1 antibodies in the imaging of MPM in preclinical models.
Supplemental material: http://radiology.rsna.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1148/radiol.12121021/-/DC1.
RSNA, 2013
Figures




Comment in
-
Science to practice: Molecular targeting with SPECT/CT and MR imaging in oncology--integration of functional and structural imaging.Radiology. 2013 Apr;267(1):1-3. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12122734. Radiology. 2013. PMID: 23525713 No abstract available.
References
-
- Raja S, Murthy SC, Mason DP. Malignant pleural mesothelioma. Curr Oncol Rep 2011;13(4):259–264 - PubMed
-
- Marom EM, Erasmus JJ, Pass HI, Patz EF., Jr The role of imaging in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Semin Oncol 2002;29(1):26–35 - PubMed
-
- Gill RR. Imaging of mesothelioma. Recent Results Cancer Res 2011;189:27–43 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

