Surgical-orthodontic management of bilateral multiple impactions in non-syndromic patient
- PMID: 23329714
- PMCID: PMC3604491
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2012-007748
Surgical-orthodontic management of bilateral multiple impactions in non-syndromic patient
Abstract
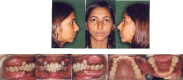
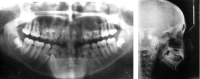
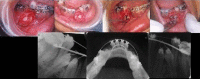
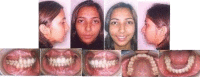
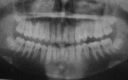
Several surgical and orthodontic treatment options are available to disimpact the impacted teeth. But the closed eruption technique has the best long-term prognosis. The tooth is surgically exposed, an attachment is bonded to it, flap is resutured over it and an orthodontic extrusive force is delivered to bring the tooth into occlusion. This case report presents a case with multiple impacted teeth in which no syndrome or systemic conditions were detected. A 20-year-old female patient reported for orthodontic treatment with chief complaint of multiple unerupted permanent teeth and retained primary teeth. Radiographic examination revealed impacted 14, 15, 24, 25, 33, 34, 43 and 44. Surgical exposure of the impacted teeth was done after extraction of retained primary teeth. Forced eruption of these teeth was done by applying traction with closed eruption technique. After careful treatment planning followed by guided eruption of impacted teeth, patient finished with a significantly improved functional and aesthetic result.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Successful treatment of multiple bilateral impactions - a case report.Head Face Med. 2016 Jul 25;12(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13005-016-0122-0. Head Face Med. 2016. PMID: 27457490 Free PMC article.
-
Maxillary canine impactions related to impacted central incisors: two case reports.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2007 Sep 1;8(6):72-81. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2007. PMID: 17846674
-
Outcomes of the surgical exposure, bonding and eruption of 82 impacted maxillary canines.J Can Dent Assoc. 1998 Sep;64(8):572-4, 576-9. J Can Dent Assoc. 1998. PMID: 9785687
-
Forced eruption of a labially impacted maxillary canine with a transcoronal stainless wire: report of case.ASDC J Dent Child. 2000 Jul-Aug;67(4):288-92. ASDC J Dent Child. 2000. PMID: 10997247 Review.
-
Surgical Treatment of Impacted Canines: What the Orthodontist Would Like the Surgeon to Know.Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2015 Aug;27(3):449-58. doi: 10.1016/j.coms.2015.04.007. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2015. PMID: 26231817 Review.
References
-
- Andreasen JO, Pindborg JJ, Hjorting-Hansen E, et al. Oral health care: more than caries and periodontal disease. A survey of epidemiological studies on oral disease. Int Dent J 1986;36:207–14 - PubMed
-
- Shroff B. Canine impaction diagnosis, treatment planning, and clinical management. In: Nanda R.ed. Biomechanics in clinical orthodontics. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, 1997:99–108
-
- Bishara SE. Clinical management of impacted maxillary canines. Semin Orthod 1998;4:87–98 - PubMed
-
- Becker A, Sharabi S, Chaushu S. Maxillary tooth size variation in dentitions with palatal canine displacement. Eur J Orthod 2002;24:313–18 - PubMed
-
- Langberg BJ, Peck S. Adequacy of maxillary dental arch width in patients with palatally displaced canines. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2000;118:220–3 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources