Flourishing Across Europe: Application of a New Conceptual Framework for Defining Well-Being
- PMID: 23329863
- PMCID: PMC3545194
- DOI: 10.1007/s11205-011-9966-7
Flourishing Across Europe: Application of a New Conceptual Framework for Defining Well-Being
Abstract
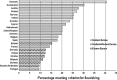
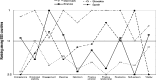
Governments around the world are recognising the importance of measuring subjective well-being as an indicator of progress. But how should well-being be measured? A conceptual framework is offered which equates high well-being with positive mental health. Well-being is seen as lying at the opposite end of a spectrum to the common mental disorders (depression, anxiety). By examining internationally agreed criteria for depression and anxiety (DSM and ICD classifications), and defining the opposite of each symptom, we identify ten features of positive well-being. These combine feeling and functioning, i.e. hedonic and eudaimonic aspects of well-being: competence, emotional stability, engagement, meaning, optimism, positive emotion, positive relationships, resilience, self esteem, and vitality. An operational definition of flourishing is developed, based on psychometric analysis of indicators of these ten features, using data from a representative sample of 43,000 Europeans. Application of this definition to respondents from the 23 countries which participated in the European Social Survey (Round 3) reveals a four-fold difference in flourishing rate, from 41% in Denmark to less than 10% in Slovakia, Russia and Portugal. There are also striking differences in country profiles across the 10 features. These profiles offer fresh insight into cultural differences in well-being, and indicate which features may provide the most promising targets for policies to improve well-being. Comparison with a life satisfaction measure shows that valuable information would be lost if well-being was measured by life satisfaction. Taken together, our findings reinforce the need to measure subjective well-being as a multi-dimensional construct in future surveys.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (l994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. revised. DSM-IV. Washington, DC: Author.
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed., Text Revision). Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association.
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2011). D05 mixed anxiety/depression. Retrieved January 26, 2011 from http://www.dsm5.org/ProposedRevisions/.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources