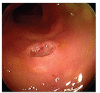
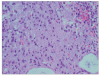
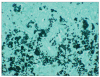
Colonic histoplasmosis
Figures
References
-
- Kauffman CA, Israel KS, Smith JW, et al. Histoplasmosis in immunosuppressed patients. Am J Med. 1978;64:923–932. - PubMed
-
- Anand A. Diagnosis of systemic histoplasmosis in AIDS patients. South Med J. 1993;86:844–845. - PubMed
-
- Cappell MS, Mandell W, Grimes MM, Neu HC. Gastrointestinal histoplasmosis. Dig Dis Sci. 1988;33:353–360. - PubMed
-
- Medoff G, Kobayashi GS. Systemic fungal infections: an overview. Hosp Pract. 1991;26:41–52. - PubMed
-
- Wheat LJ, Smith EJ, Sathapatayavongs B, et al. Histoplasmosis in renal allograft recipients. Arch Intern Med. 1983;143:703–707. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources