Comparison of different modalities for reducing childhood intussusception
- PMID: 23329922
- PMCID: PMC3522312
Comparison of different modalities for reducing childhood intussusception
Abstract
Background/objective: Idiopathic intussusception is an important abdominal emergency in infancy and childhood. Non operative management for treatment is firstly considered due to less invasiveness, less complications and cost effectiveness compared to surgical treatment. This study summarizes our experience in the management of intussusception in children who were referred to a children hospital.
Patients and methods: A total of 102 children who were diagnosed as having intussusception were referred to one children hospital in Tehran during a period of 10 years, from 1997 to 2007. Reductions were performed upon 57 cases by a radiologist or radiology residents, if there was no medical contraindication. We used chi-square test for analysis.
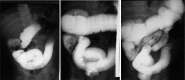
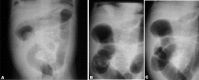
Results: The success rate of reduction was eight out of 13 (61.5%) with barium, nine out of 17 (53.5%) with air and 22 out of 27 (81.5%) with saline (p value=0.116). One patient had recurrence with air reduction. Another case was complicated by peritonitis using barium enema.
Conclusion: There was no significant relationship between the success rate of reduction and the type of reduction.
Keywords: Children; Intussusception; Invagination.
Figures


References
-
- Buonomo C, Taylor GA, Share JC, Kirks DR. Gastrointestinal tract. In: Kirks DR, Griscom NT, editors. Practical pediatric imaging: diagnostic radiology of infants and children. New York: Lippincott Wiliams & Wilkins; 1998. pp. 915–16.
-
- Yoon CH, Kim HJ, Goo HW. Intussusception in children: US-guided pneumatic reduction--initial experience. Radiology. 2001 Jan;218(1):85–8. - PubMed
-
- Bartton SL, Haberkern CM, Waldhausen J, Sawin RS, Allison JW. Intussusception: hospital size and risk of surgery. Pediatrics. 2001 Feb;107(2):299–303. - PubMed
-
- Daneman A, Alton DJ, Ein S, Wesson D, Superina R, Thorner P. Perforation during attempted intussusception reduction in children-a comparison of perforation with barium and air. Pediatr Radiol. 1995;25(2):81–8. - PubMed
-
- Wood SK, Kim JS, Suh SJ, Paik TW, Choi SO. Childhood intussusception: US-guided hydrostatic reduction. Radiology. 1992 Jan;182(1):77–80. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
