Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition negatively affects muscle stem cell behavior
- PMID: 23329998
- PMCID: PMC3544228
Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition negatively affects muscle stem cell behavior
Abstract
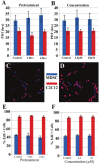
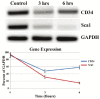
Skeletal muscle is a large and complex system that is crucial for structural support, movement and function. When injured, the repair of skeletal muscle undergoes three phases: inflammation and degeneration, regeneration and fibrosis formation in severe injuries. During fibrosis formation, muscle healing is impaired because of the accumulation of excess collagen. A group of zinc-dependent endopeptidases that have been found to aid in the repair of skeletal muscle are matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). MMPs are able to assist in tissue remodeling through the regulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) components, as well as contributing to cell migration, proliferation, differentiation and angiogenesis. In the present study, the effect of GM6001, a broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor, on muscle-derived stem cells (MDSCs) is investigated. We find that MMP inhibition negatively impacts skeletal muscle healing by impairing MDSCs in migratory and multiple differentiation abilities. These results indicate that MMP signaling plays an essential role in the wound healing of muscle tissue because their inhibition is detrimental to stem cells residing in skeletal muscle.
Keywords: MMPs; Skeletal muscle stem cells; cell migration; differentiation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Matrix metalloproteinase 13 is a new contributor to skeletal muscle regeneration and critical for myoblast migration.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Sep;305(5):C529-38. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00051.2013. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23761625 Free PMC article.
-
MMP inhibition as a potential method to augment the healing of skeletal muscle and tendon extracellular matrix.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013 Sep;115(6):884-91. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00137.2013. Epub 2013 May 2. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013. PMID: 23640595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining the role of mesenchymal stromal cells on the regulation of matrix metalloproteinases in skeletal muscle cells.Exp Cell Res. 2014 May 1;323(2):297-313. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.03.003. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Exp Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24631289
-
Role of matrix metalloproteinases in skeletal muscle: migration, differentiation, regeneration and fibrosis.Cell Adh Migr. 2009 Oct-Dec;3(4):337-41. doi: 10.4161/cam.3.4.9338. Epub 2009 Oct 24. Cell Adh Migr. 2009. PMID: 19667757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monocyte-derived dendritic cell subpopulations use different types of matrix metalloproteinases inhibited by GM6001.Immunobiology. 2013 Nov;218(11):1361-9. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.06.012. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23870824
Cited by
-
MMP1 gene expression enhances myoblast migration and engraftment following implanting into mdx/SCID mice.Cell Adh Migr. 2015;9(4):283-92. doi: 10.4161/19336918.2014.983799. Cell Adh Migr. 2015. PMID: 26223276 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA within myofibers controls satellite cell microenvironment to allow hypertrophic growth.iScience. 2021 Dec 11;25(1):103616. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103616. eCollection 2022 Jan 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 35106464 Free PMC article.
-
FGF2-induced effects on transcriptome associated with regeneration competence in adult human fibroblasts.BMC Genomics. 2013 Sep 26;14:656. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-656. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24066673 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin K activity controls cardiotoxin-induced skeletal muscle repair in mice.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018 Feb;9(1):160-175. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12248. Epub 2017 Oct 23. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018. PMID: 29058826 Free PMC article.
-
Fat deposition and accumulation in the damaged and inflamed skeletal muscle: cellular and molecular players.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Jun;72(11):2135-56. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1857-7. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25854633 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Charge SB, Rudnicki MA. Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:209–38. - PubMed
-
- Grefte S, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM, Torensma R, Von den Hoff JW. Skeletal muscle development and regeneration. Stem Cells Dev. 2007;16:857–68. - PubMed
-
- Huard J, Li Y, Fu FH. Muscle injuries and repair: current trends in research. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A:822–32. - PubMed
-
- Nozaki M, Li Y, Zhu J, Ambrosio F, Uehara K, Fu FH, Huard J. Improved muscle healing after contusion injury by the inhibitory effect of suramin on myostatin, a negative regulator of muscle growth. Am J Sports Med. 2008;36:2354–62. - PubMed
-
- Ritenour AE, Christy RJ, Roe JL, Baer DG, Dubick MA, Wade CE, Holcomb JB, Walters TJ. The Effect of a Hypobaric, Hypoxic Environment on Acute Skeletal Muscle Edema after Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Journal of Surgical Research. 2010;160:253–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
