Nuclear receptors in bile acid metabolism
- PMID: 23330546
- PMCID: PMC3676171
- DOI: 10.3109/03602532.2012.740048
Nuclear receptors in bile acid metabolism
Abstract
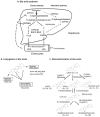
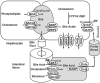
Bile acids are signaling molecules that activate nuclear receptors, such as farnesoid X receptor, pregnane X receptor, constitutive androstane receptor, and vitamin D receptor, and play a critical role in the regulation of lipid, glucose, energy, and drug metabolism. These xenobiotic/endobiotic-sensing nuclear receptors regulate phase I oxidation, phase II conjugation, and phase III transport in bile acid and drug metabolism in the digestive system. Integration of bile acid metabolism with drug metabolism controls absorption, transport, and metabolism of nutrients and drugs to maintain metabolic homeostasis and also protects against liver injury, inflammation, and related metabolic diseases, such as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, diabetes, and obesity. Bile-acid-based drugs targeting nuclear receptors are in clinical trials for treating cholestatic liver diseases and fatty liver disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nuclear Receptor Metabolism of Bile Acids and Xenobiotics: A Coordinated Detoxification System with Impact on Health and Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 17;19(11):3630. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113630. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30453651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xenobiotic-sensing nuclear receptors involved in drug metabolism: a structural perspective.Drug Metab Rev. 2013 Feb;45(1):79-100. doi: 10.3109/03602532.2012.740049. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Drug Metab Rev. 2013. PMID: 23210723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in xenobiotic metabolism in the long-lived Little mice.Aging Cell. 2007 Aug;6(4):453-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00300.x. Epub 2007 May 23. Aging Cell. 2007. PMID: 17521389 Free PMC article.
-
Bile acid receptors FXR and TGR5 signaling in fatty liver diseases and therapy.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Mar 1;318(3):G554-G573. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00223.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31984784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of phase I, II and III drug metabolism/transport by xenobiotics.Arch Pharm Res. 2005 Mar;28(3):249-68. doi: 10.1007/BF02977789. Arch Pharm Res. 2005. PMID: 15832810 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of berberine on hyperglycaemia and gut microbiota composition in type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Feb 28;27(8):708-724. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i8.708. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33716449 Free PMC article.
-
Role of bile acids and their receptors in gastrointestinal and hepatic pathophysiology.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jul;19(7):432-450. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00566-7. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35165436 Review.
-
Crosstalk between FXR and TGR5 controls glucagon-like peptide 1 secretion to maintain glycemic homeostasis.Lab Anim Res. 2018 Dec;34(4):140-146. doi: 10.5625/lar.2018.34.4.140. Epub 2018 Dec 31. Lab Anim Res. 2018. PMID: 30671099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatoprotective Effects of Glycyrrhetinic Acid on Lithocholic Acid-Induced Cholestatic Liver Injury Through Choleretic and Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 31;13:881231. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.881231. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35712714 Free PMC article.
-
Fasting-sensitive SUMO-switch on Prox1 controls hepatic cholesterol metabolism.EMBO Rep. 2023 Oct 9;24(10):e55981. doi: 10.15252/embr.202255981. Epub 2023 Aug 10. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 37560809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ananthanarayanan M, Balasubramanian N, Makishima M, Mangelsdorf DJ, Suchy FJ. Human bile salt export pump promoter is transactivated by the farnesoid X receptor/bile acid receptor. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:28857–28865. - PubMed
-
- Arrese M, Trauner M, Sacchiero RJ, Crossman MW, Shneider BL. Neither intestinal sequestration of bile acids nor common bile duct ligation modulate the expression and function of the rat ileal bile acid transporter. Hepatology. 1998;28:1081–1087. - PubMed
-
- Berge KE, Tian H, Graf GA, Yu L, Grishin NV, Schultz J, et al. Accumulation of dietary cholesterol in sitosterolemia caused by mutations in adjacent ABC transporters. Science. 2000;290:1771–1775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
