Complexity generation in fungal peptidyl alkaloid biosynthesis: a two-enzyme pathway to the hexacyclic MDR export pump inhibitor ardeemin
- PMID: 23330675
- PMCID: PMC3631443
- DOI: 10.1021/cb3006787
Complexity generation in fungal peptidyl alkaloid biosynthesis: a two-enzyme pathway to the hexacyclic MDR export pump inhibitor ardeemin
Abstract
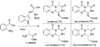
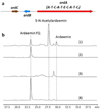
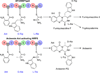
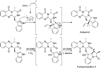
Ardeemins are hexacyclic peptidyl alkaloids isolated from Aspergillus fischeri as agents that block efflux of anticancer drugs by MultiDrug Resistance (MDR) export pumps. To evaluate the biosynthetic logic and enzymatic machinery for ardeemin framework assembly, we sequenced the A. fischeri genome and identified the ardABC gene cluster. Through both genetic deletions and biochemical characterizations of purified ArdA and ArdB we show this ArdAB enzyme pair is sufficient to convert anthranilate (Ant), L-Ala, and L-Trp to ardeemin. ArdA is a 430 kDa trimodular nonribosomal peptide synthase (NRPS) that converts the three building blocks into a fumiquinazoline (FQ) regioisomer termed ardeemin FQ. ArdB is a prenyltransferase that takes tricyclic ardeemin FQ and dimethylallyl diphosphate to the hexacyclic ardeemin scaffold via prenylation at C2 of the Trp-derived indole moiety with intramolecular capture by an amide NH of the fumiquinazoline ring. The two-enzyme ArdAB pathway reveals remarkable efficiency in construction of the hexacyclic peptidyl alkaloid scaffold.
Figures

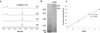
References
-
- Fremlin LJ, Piggott AM, Lacey E, Capon RJ. Cottoquinazoline A and cotteslosins A and B, metabolites from an Australian marine-derived strain of Aspergillus versicolor. J. Nat. Prod. 2009;72:666–670. - PubMed
-
- Jiao RH, Xu S, Liu JY, Ge HM, Ding H, Xu C, Zhu HL, Tan RX. Chaetominine, a Cytotoxic Alkaloid Produced by Endophytic Chaetomium sp. IFBE015. Org. Lett. 2006;8:5709–5712. - PubMed
-
- Wong SM, Musza LL, Kydd GC, Kullnig R, Gillum AM, Cooper R. Fiscalins: new substance P inhibitors produced by the fungus Neosartorya fischeri. Taxonomy, fermentation, structures, and biological properties. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1993;46:545–553. - PubMed
-
- Walsh CT, Haynes SW, Ames BD. Aminobenzoates as building blocks for natural product assembly lines. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012;29:37–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

