Signaling by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase family in immune cells
- PMID: 23330955
- PMCID: PMC4516760
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-095946
Signaling by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase family in immune cells
Abstract
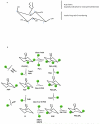
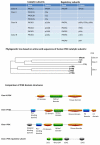
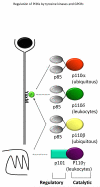
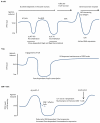
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks) control many important aspects of immune cell development, differentiation, and function. Mammals have eight PI3K catalytic subunits that are divided into three classes based on similarities in structure and function. Specific roles for the class I PI3Ks have been broadly investigated and are relatively well understood, as is the function of their corresponding phosphatases. More recently, specific roles for the class II and class III PI3Ks have emerged. Through vertebrate evolution and in parallel with the evolution of adaptive immunity, there has been a dramatic increase not only in the genes for PI3K subunits but also in genes for phosphatases that act on 3-phosphoinositides and in 3-phosphoinositide-binding proteins. Our understanding of the PI3Ks in immunity is guided by fundamental discoveries made in simpler model organisms as well as by appreciating new adaptations of this signaling module in mammals in general and in immune cells in particular.
Figures

References
-
- Hawkins PT, Anderson KE, Davidson K, Stephens LR. Signalling through Class I PI3Ks in mammalian cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006;34:647–62. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:606–19. - PubMed
-
- Vanhaesebroeck B, Guillermet-Guibert J, Graupera M, Bilanges B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:329–41. - PubMed
-
- Vanhaesebroeck B, Leevers SJ, Panayotou G, Waterfield MD. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases: a conserved family of signal transducers. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:267–72. - PubMed
-
- Backer JM. The regulation and function of Class III PI3Ks: novel roles for Vps34. Biochem J. 2008;410:1–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 095691/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/C509890/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/B/0000M979/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/F015461/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- JF19128/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

