Effectiveness of daily versus non-daily granulocyte colony-stimulating factors in patients with solid tumours undergoing chemotherapy: a multivariate analysis of data from current practice
- PMID: 23331323
- PMCID: PMC3655543
- DOI: 10.1111/ecc.12043
Effectiveness of daily versus non-daily granulocyte colony-stimulating factors in patients with solid tumours undergoing chemotherapy: a multivariate analysis of data from current practice
Abstract
We conducted a multicentre, retrospective, observational study including patients with solid tumours (excluding breast cancer) that received granulocyte colony-stimulating factors (G-CSF) and chemotherapy. We investigated the effectiveness of daily vs. non-daily G-CSFs (pegfilgrastim) adjusting by potential confounders. The study included 391 patients (211 daily G-CSF; 180 pegfilgrastim), from whom 47.3% received primary prophylaxis (PP) (57.8% pegfilgrastim), 26.3% secondary prophylaxis (SP: initiation after cycle 1 and no reactive treatment in any cycle) (51.5% pegfilgrastim) and 26.3% reactive treatment (19.4% pegfilgrastim). Only 42.2% of patients with daily G-CSF and 46.2% with pegfilgrastim initiated prophylaxis within 72 h after chemotherapy, and only 10.5% of patients with daily G-CSF received it for ≥ 7 days. In the multivariate models, daily G-CSF was associated with higher risk of grade 3-4 neutropenia (G3-4N) vs. pegfilgrastim [odds ratio (OR): 1.73, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.004-2.97]. Relative to SP, PP protected against G3-4N (OR for SP vs. PP: 6.0, 95%CI: 3.2-11.4) and febrile neutropenia (OR: 3.1, 95%CI: 1.1-8.8), and was associated to less chemotherapy dose delays and reductions (OR for relative dose intensity <85% for SP vs. PP: 3.1, 95%CI: 1.7-5.4) and higher response rate (OR: 2.1, 95%CI: 1.2-3.7). Data suggest that pegfilgrastim, compared with a daily G-CSF, and PP, compared with SP, could be more effective in preventing neutropenia and its related events in the clinical practice.
© 2013 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
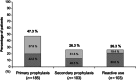
 , Pegfilgrastim;
, Pegfilgrastim;  , Daily G-CSF. G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factors.
, Daily G-CSF. G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factors.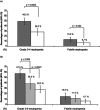
 , Daily G-CSF;
, Daily G-CSF;  , Pegfilgrastim. (b) daily G-CSF (<5 days or ≥5 days) or pegfilgrastim.
, Pegfilgrastim. (b) daily G-CSF (<5 days or ≥5 days) or pegfilgrastim.  , Daily G-CSF (<5 days);
, Daily G-CSF (<5 days);  , Daily G-CSF (≥5 days);
, Daily G-CSF (≥5 days);  , Pegfilgrastim. G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factors.
, Pegfilgrastim. G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factors.References
-
- Aapro MS, Cameron DA, Pettengell R, Bohlius J, Crawford J, Ellis M, Kearney N, Lyman GH, Tjan-Heijnen VC, Walewski J, Weber DC, Zielinski C. EORTC guidelines for the use of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia in adult patients with lymphomas and solid tumours. European Journal of Cancer. 2006;42:2433–2453. - PubMed
-
- Almenar D, Mayans J, Juan O, Bueno JM, Lopez JI, Frau A, Guinot M, Cerezuela P, Buscalla EG, Gasquet JA, Sanchez J. Pegfilgrastim and daily granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: patterns of use and neutropenia-related outcomes in cancer patients in Spain – results of the LEARN Study. European Journal of Cancer Care. 2009;18:280–286. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bishop MR, Tarantolo SR, Geller RB, Lynch JC, Bierman PJ, Pavletic ZS, Vose JM, Kruse S, Dix SP, Morris ME, Armitage JO, Kessinger A. A randomized, double-blind trial of filgrastim (granulocyte colony-stimulating factor) versus placebo following allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2000;96:80–85. - PubMed
-
- Bui BN, Chevallier B, Chevreau C, Krakowski I, Peny AM, Thyss A, Maugard-Louboutin C, Cupissol D, Fargeot P, Bonichon F, et al. Efficacy of lenograstim on hematologic tolerance to MAID chemotherapy in patients with advanced soft tissue sarcoma and consequences on treatment dose-intensity. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 1995;13:2629–2636. - PubMed
-
- Cámara JIM, Pousa AL, García EG, Llach XB, Surinyach NL, Vilela FS, Liu Z, Arocho R. Evaluación económica del uso de pegfilgrastim frente a filgrastim en profilaxis primaria en pacientes con cáncer de mama con riesgo de padecer neutropenia febril en España. PharmacoEconomics. 2008;5:71–81.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

