The effects of taurolidine alone and in combination with doxorubicin or carboplatin in canine osteosarcoma in vitro
- PMID: 23331343
- PMCID: PMC3551657
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-6148-9-15
The effects of taurolidine alone and in combination with doxorubicin or carboplatin in canine osteosarcoma in vitro
Abstract
Background: Osteosarcoma (OS) affects over 8000 dogs/year in the United States. The disease usually arises in the appendicular skeleton and metastasizes to the lung. Dogs with localized appendicular disease benefit from limb amputation and chemotherapy but most die within 6-12 months despite these treatments. Taurolidine, a derivative of taurine, has anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic effects against a variety of cancers. The following in vitro studies tested taurolidine as a candidate for adjuvant therapy for canine OS. Tests for p53 protein status and caspase activity were used to elucidate mechanisms of taurolidine-induced cell death.
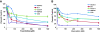
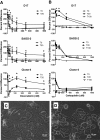
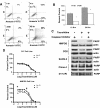
Results: Taurolidine was cytotoxic to osteosarcoma cells and increased the toxicity of doxorubicin and carboplatin in vitro. Apoptosis was greatly induced in cells exposed to 125 μM taurolidine and less so in cells exposed to 250 μM taurolidine. Taurolidine cytotoxicity appeared caspase-dependent in one cell line; with apparent mutant p53 protein. This cell line was the most sensitive to single agent taurolidine treatment and had a taurolidine-dependent reduction in accumulated p53 protein suggesting taurolidine's effects may depend on the functional status of p53 in canine OS.
Conclusion: Taurolidine's cytotoxic effect appears dependent on cell specific factors which may be explained, in part, by the functional status of p53. Taurolidine initiates apoptosis in canine OS cells and this occurs to a greater extent at lower concentrations. Mechanisms of cell death induced by higher concentrations were not elucidated here. Taurolidine combined with doxorubicin or carboplatin can increase the toxicity of these chemotherapy drugs and warrants further investigation in dogs with osteosarcoma.
Figures


References
-
- Imhof L, Goldinger SM, Baumann K, Schad K, French LE, Rothlisberger P, Dummer R. The antibacterial substance, taurolidine in the second/third-line treatment of very advanced stage IV melanoma including brain metastases: results of a phase 2, open-label study. Melanoma Res. 2011;21(1):80–83. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0b013e328341442d. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chromik AM, Daigeler A, Bulut D, Flier A, May C, Harati K, Roschinsky J, Sulberg D, Ritter PR, Mittelkotter U. et al.Comparative analysis of cell death induction by Taurolidine in different malignant human cancer cell lines. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010;29:21. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-21. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

