Hypothalamic tanycytes: potential roles in the control of feeding and energy balance
- PMID: 23332797
- PMCID: PMC3605593
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2012.12.008
Hypothalamic tanycytes: potential roles in the control of feeding and energy balance
Abstract
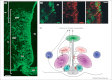
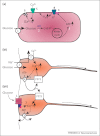
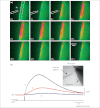
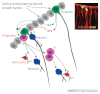
Tanycytes, glial-like cells that line the third ventricle, are emerging as components of the hypothalamic networks that control body weight and energy balance. They contact the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and send processes that come into close contact with neurons in the arcuate and ventromedial hypothalamic nuclei. Tanycytes are glucosensitive and are able to respond to transmitters associated with arousal and the drive to feed. At least some tanycytes are stem cells and, in the median eminence, may be stimulated by diet to generate new neurons. The quest is on to understand how tanycytes detect and respond to changes in energy balance and how they communicate with the rest of the nervous system to effect their functions.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Morton G.J. Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature. 2006;443:289–295. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez E.M. Hypothalamic tanycytes: a key component of brain–endocrine interaction. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2005;247:89–164. - PubMed
-
- Mathew T.C. Regional analysis of the ependyma of the third ventricle of rat by light and electron microscopy. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2008;37:9–18. - PubMed
-
- Vigh B. Cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons of the central canal and terminal ventricle in various vertebrates. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;231:615–621. - PubMed
-
- Vigh B., Vigh-Teichmann I. Actual problems of the cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1998;41:57–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

