Liver injury from tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists: analysis of thirty-four cases
- PMID: 23333219
- PMCID: PMC3865702
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2012.12.025
Liver injury from tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists: analysis of thirty-four cases
Abstract
Background & aims: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α antagonists have been associated with drug-induced liver injury (DILI). We reviewed cases of DILI in the United States to identify those associated with use of TNF-α antagonists.
Methods: We searched the U.S. DILI Network (DILIN) database, from 2003 to 2011, for cases associated with TNF-α antagonists. Mean Roussel-Uclaf Causality Assessment Method scores were calculated. A DILIN severity score was assigned according to a previously published scale, and we identified 6 subjects likely to have DILI associated with use of TNF-α antagonists. We also searched PubMed for articles that reported hepatotoxicity from TNF-α antagonists, identifying 28 additional cases suitable for analysis.
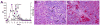
Results: The drugs presumed to have caused DILI were infliximab (n = 26), etanercept (n = 4), and adalimumab (n = 4). The anti-TNF-α agent was the probable cause of 12 cases of DILI (35%), a very likely cause for 21 (62%), and a definite cause for 1 (3%). Median latency was 13 weeks (range, 2-104); however, 7 cases (20%) had latency periods longer than 24 weeks. Twenty-two of 33 subjects who underwent serologic analysis (67%) tested positive for anti-nuclear and/or smooth muscle antibodies. Of these 22, 17 underwent liver biopsy; 15 subjects had clear features of autoimmunity. The 22 subjects with autoimmune features had longer median latency (16 vs 10 weeks) and higher peak levels of alanine aminotransferase (784 vs 528 U/L) than the 12 without such features. There was 1 case of severe cholestasis. All but one subject improved after discontinuation of the implicated drug; 12 subjects received corticosteroid therapy. No deaths were attributed to liver injury, although one patient with preexistent cirrhosis required liver transplantation.
Conclusions: Acute liver injury caused by TNF-α antagonists may be a class effect because multiple agents in this category have been implicated. The most common presentation is an autoimmune phenotype with marked hepatocellular injury, but a mixed non-autoimmune pattern or predominant cholestasis also occurs. The prognosis is usually good after drug discontinuation, although some patients may benefit from a course of corticosteroids. ClinicalTrials.gov: Number, NCT00345930.
Copyright © 2013 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures
References
-
- Bezabeh S, Flowers C, Kortepeter C, et al. Clinically significant liver injury in patients treated with natalizumab. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;31:1028–1035. - PubMed
-
- Davern T. Hepatotoxicity of immunomodulator agents and the transplant situation. In: Kaplowitz N, Deleve L, editors. Drug-induced liver injury. New York: Informa Helathcare; 2007.
-
- Carroll MB, Bond MI. Use of tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2008;38:208–217. - PubMed
-
- FDA. [Accessed November 2011.];Briefing document: Arthritis Advisory Committee. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/03/transcripts/3930T1.htm.
-
- García Aparicio A, Rey J, Sanz A, et al. Successful treatment with etanercept in a patient with hepatotoxicity closely related to infliximab. Clin Rheumatol. 2007;26:811–813. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 DK065211/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01DK065238/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01DK065021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK065193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK083027/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK083020/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065201/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065238/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01DK065201/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065176/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK083023/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01DK065176/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01DK065193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01DK065211/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01DK065184/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065184/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

