Structure of glutaraldehyde cross-linked ryanodine receptor
- PMID: 23333333
- PMCID: PMC3587655
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsb.2013.01.001
Structure of glutaraldehyde cross-linked ryanodine receptor
Abstract
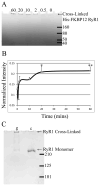
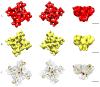
The ryanodine receptor (RyR) family of calcium release channels plays a vital role in excitation-contraction coupling (ECC). Along with the dihydropyridine receptor (DHPR), calsequestrin, and several other smaller regulatory and adaptor proteins, RyRs form a large dynamic complex referred to as ECC machinery. Here we describe a simple cross-linking procedure that can be used to stabilize fragile components of the ECC machinery, for the purpose of structural elucidation by single particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). As a model system, the complex of the FK506-binding protein (FKBP12) and RyR1 was used to test the cross-linking protocol. Glutaraldehyde fixation led to complete cross-linking of receptor-bound FKBP12 to RyR1, and also to extensive cross-linking of the four subunits comprising RyR to one another without compromising the RyR1 ultrastructure. FKBP12 cross-linked with RyR1 was visualized in 2D averages by single particle cryo-EM. Comparison of control RyR1 and cross-linked RyR1 3D reconstructions revealed minor conformational changes at the transmembrane assembly and at the cytoplasmic region. Intersubunit cross-linking enhanced [(3)H]ryanodine binding to RyR1. Based on our findings we propose that intersubunit cross-linking of RyR1 by glutaraldehyde induced RyR1 to adopt an open like conformation.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Aghdasi B, Zhang J, Wu Y, Reid MB, Hamilton SL. Multiple classes of sulfhydryls modulate the skeletal muscle Ca2+ release channel. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:3739–3748. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

