Mutual expression of the transcription factors Runx3 and ThPOK regulates intestinal CD4⁺ T cell immunity
- PMID: 23334789
- PMCID: PMC3804366
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2518
Mutual expression of the transcription factors Runx3 and ThPOK regulates intestinal CD4⁺ T cell immunity
Abstract
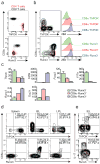
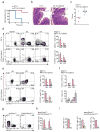
The gut mucosa hosts large numbers of activated lymphocytes that are exposed to stimuli from the diet, microbiota and pathogens. Although CD4(+) T cells are crucial for defense, intestinal homeostasis precludes exaggerated responses to luminal contents, whether they are harmful or not. We investigated mechanisms used by CD4(+) T cells to avoid excessive activation in the intestine. Using genetic tools to label and interfere with T cell-development transcription factors, we found that CD4(+) T cells acquired the CD8-lineage transcription factor Runx3 and lost the CD4-lineage transcription factor ThPOK and their differentiation into the T(H)17 subset of helper T cells and colitogenic potential, in a manner dependent on transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and retinoic acid. Our results demonstrate considerable plasticity in the CD4(+) T cell lineage that allows chronic exposure to luminal antigens without pathological inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
Figures






Comment in
-
T cells: The plastic virtues of a CD4+ T cell.Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 Mar;13(3):151. doi: 10.1038/nri3400. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23370307 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

