Analysis of CDS-located miRNA target sites suggests that they can effectively inhibit translation
- PMID: 23335364
- PMCID: PMC3613578
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.139758.112
Analysis of CDS-located miRNA target sites suggests that they can effectively inhibit translation
Abstract
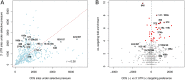
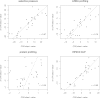
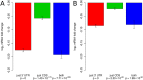
Most of what is presently known about how miRNAs regulate gene expression comes from studies that characterized the regulatory effect of miRNA binding sites located in the 3' untranslated regions (UTR) of mRNAs. In recent years, there has been increasing evidence that miRNAs also bind in the coding region (CDS), but the implication of these interactions remains obscure because they have a smaller impact on mRNA stability compared with miRNA-target interactions that involve 3' UTRs. Here we show that miRNA-complementary sites that are located in both CDS and 3'-UTRs are under selection pressure and share the same sequence and structure properties. Analyzing recently published data of ribosome-protected fragment profiles upon miRNA transfection from the perspective of the location of miRNA-complementary sites, we find that sites located in the CDS are most potent in inhibiting translation, while sites located in the 3' UTR are more efficient at triggering mRNA degradation. Our study suggests that miRNAs may combine targeting of CDS and 3' UTR to flexibly tune the time scale and magnitude of their post-transcriptional regulatory effects.
Figures


References
-
- Alexiou P, Maragkakis M, Papadopoulos GL, Reczko M, Hatzigeorgiou AG 2009. Lost in translation: An assessment and perspective for computational microRNA target identification. Bioinformatics 25: 3049–3055 - PubMed
-
- Bagga S, Bracht J, Hunter S, Massirer K, Holtz J, Eachus R, Pasquinelli AE 2005. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell 122: 553–563 - PubMed
-
- Balatti V, Maniero S, Ferracin M, Veronese A, Negrini M, Ferrocci G, Martini F, Tognon MG 2011. MicroRNAs dysregulation in human malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Thorac Oncol 6: 844–851 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
