Efficacy of vitamin and antioxidant supplements in prevention of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
- PMID: 23335472
- PMCID: PMC3548618
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.f10
Efficacy of vitamin and antioxidant supplements in prevention of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Abstract
Objective: To assess the efficacy of vitamin and antioxidant supplements in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Design: Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.
Data sources and study selection: PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, Scopus, CINAHL, and ClinicalTrials.gov searched in June and November 2012. Two authors independently reviewed and selected eligible randomised controlled trials, based on predetermined selection criteria.
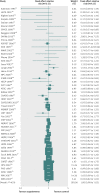
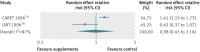
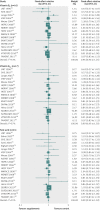
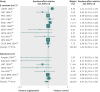
Results: Out of 2240 articles retrieved from databases and relevant bibliographies, 50 randomised controlled trials with 294,478 participants (156,663 in intervention groups and 137,815 in control groups) were included in the final analyses. In a fixed effect meta-analysis of the 50 trials, supplementation with vitamins and antioxidants was not associated with reductions in the risk of major cardiovascular events (relative risk 1.00, 95% confidence interval 0.98 to 1.02; I(2)=42%). Overall, there was no beneficial effect of these supplements in the subgroup meta-analyses by type of prevention, type of vitamins and antioxidants, type of cardiovascular outcomes, study design, methodological quality, duration of treatment, funding source, provider of supplements, type of control, number of participants in each trial, and supplements given singly or in combination with other supplements. Among the subgroup meta-analyses by type of cardiovascular outcomes, vitamin and antioxidant supplementation was associated with a marginally increased risk of angina pectoris, while low dose vitamin B(6) supplementation was associated with a slightly decreased risk of major cardiovascular events. Those beneficial or harmful effects disappeared in subgroup meta-analysis of high quality randomised controlled trials within each category. Also, even though supplementation with vitamin B(6) was associated with a decreased risk of cardiovascular death in high quality trials, and vitamin E supplementation with a decreased risk of myocardial infarction, those beneficial effects were seen only in randomised controlled trials in which the supplements were supplied by the pharmaceutical industry.
Conclusion: There is no evidence to support the use of vitamin and antioxidant supplements for prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures


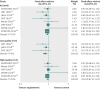
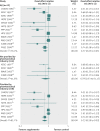
Comment in
-
ACP Journal Club. Review: vitamin and antioxidant supplements do not prevent adverse cardiovascular events.Ann Intern Med. 2013 Jun 18;158(12):JC10. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-158-12-201306180-02010. Ann Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 23778922 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mendis S, Lindholm LH, Anderson SG, Alwan A, Koju R, Onwubere BJ, et al. Total cardiovascular risk approach to improve efficiency of cardiovascular prevention in resource constrain settings. J Clin Epidemiol 2011;64:1451-62. - PubMed
-
- Dauchet L, Amouyel P, Dallongeville J. Fruits, vegetables and coronary heart disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 2009;6:599-608. - PubMed
-
- Vivekananthan DP, Penn MS, Sapp SK, Hsu A, Topol EJ. Use of antioxidant vitamins for the prevention of cardiovascular disease: meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2003;361:2017-23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
