CPAT: Coding-Potential Assessment Tool using an alignment-free logistic regression model
- PMID: 23335781
- PMCID: PMC3616698
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt006
CPAT: Coding-Potential Assessment Tool using an alignment-free logistic regression model
Abstract
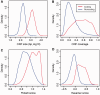
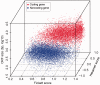
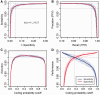
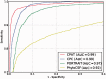
Thousands of novel transcripts have been identified using deep transcriptome sequencing. This discovery of large and 'hidden' transcriptome rejuvenates the demand for methods that can rapidly distinguish between coding and noncoding RNA. Here, we present a novel alignment-free method, Coding Potential Assessment Tool (CPAT), which rapidly recognizes coding and noncoding transcripts from a large pool of candidates. To this end, CPAT uses a logistic regression model built with four sequence features: open reading frame size, open reading frame coverage, Fickett TESTCODE statistic and hexamer usage bias. CPAT software outperformed (sensitivity: 0.96, specificity: 0.97) other state-of-the-art alignment-based software such as Coding-Potential Calculator (sensitivity: 0.99, specificity: 0.74) and Phylo Codon Substitution Frequencies (sensitivity: 0.90, specificity: 0.63). In addition to high accuracy, CPAT is approximately four orders of magnitude faster than Coding-Potential Calculator and Phylo Codon Substitution Frequencies, enabling its users to process thousands of transcripts within seconds. The software accepts input sequences in either FASTA- or BED-formatted data files. We also developed a web interface for CPAT that allows users to submit sequences and receive the prediction results almost instantly.
Figures
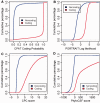
References
-
- Bertone P, Stolc V, Royce TE, Rozowsky JS, Urban AE, Zhu X, Rinn JL, Tongprasit W, Samanta M, Weissman S, et al. Global identification of human transcribed sequences with genome tiling arrays. Science (New York, NY) 2004;306:2242–2246. - PubMed
-
- Kapranov P, Cheng J, Dike S, Nix DA, Duttagupta R, Willingham AT, Stadler PF, Hertel J, Hackermüller J, Hofacker IL, et al. RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science (New York, NY) 2007;316:1484–1488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

