The yeast transcription factor Crz1 is activated by light in a Ca2+/calcineurin-dependent and PKA-independent manner
- PMID: 23335962
- PMCID: PMC3546054
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053404
The yeast transcription factor Crz1 is activated by light in a Ca2+/calcineurin-dependent and PKA-independent manner
Abstract
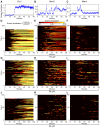
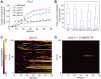
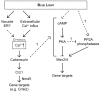
Light in the visible range can be stressful to non-photosynthetic organisms. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has earlier been reported to respond to blue light via activation of the stress-regulated transcription factor Msn2p. Environmental changes also induce activation of calcineurin, a Ca(2+)/calmodulin dependent phosphatase, which in turn controls gene transcription by dephosphorylating the transcription factor Crz1p. We investigated the connection between cellular stress caused by blue light and Ca(2+) signalling in yeast by monitoring the nuclear localization dynamics of Crz1p, Msn2p and Msn4p. The three proteins exhibit distinctly different stress responses in relation to light exposure. Msn2p, and to a lesser degree Msn4p, oscillate rapidly between the nucleus and the cytoplasm in an apparently stochastic fashion. Crz1p, in contrast, displays a rapid and permanent nuclear localization induced by illumination, which triggers Crz1p-dependent transcription of its target gene CMK2. Moreover, increased extracellular Ca(2+) levels stimulates the light-induced responses of all three transcription factors, e.g. Crz1p localizes much quicker to the nucleus and a larger fraction of cells exhibits permanent Msn2p nuclear localization at higher Ca(2+) concentration. Studies in mutants lacking Ca(2+) transporters indicate that influx of extracellular Ca(2+) is crucial for the initial stages of light-induced Crz1p nuclear localization, while mobilization of intracellular Ca(2+) stores appears necessary for a sustained response. Importantly, we found that Crz1p nuclear localization is dependent on calcineurin and the carrier protein Nmd5p, while not being affected by increased protein kinase A activity (PKA), which strongly inhibits light-induced nuclear localization of Msn2/4p. We conclude that the two central signalling pathways, cAMP-PKA-Msn2/4 and Ca(2+)-calcineurin-Crz1, are both activated by blue light illumination.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Bodvard K, Wrangborg D, Tapani S, Logg K, Sliwa P, et al. (2011) Continuous light exposure causes cumulative stress that affects the localization oscillation dynamics of the transcription factor Msn2p. BBA-Mol Cell Res 1813: 358–366. - PubMed
-
- Garmendia-Torres C, Goldbeter A, Jacquet M (2007) Nucleocytoplasmic oscillations of the yeast transcription factor Msn2: Evidence for periodic PKA activation. Current Biology 17: 1044–1049. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

