Differential processing of let-7a precursors influences RRM2 expression and chemosensitivity in pancreatic cancer: role of LIN-28 and SET oncoprotein
- PMID: 23335963
- PMCID: PMC3546076
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053436
Differential processing of let-7a precursors influences RRM2 expression and chemosensitivity in pancreatic cancer: role of LIN-28 and SET oncoprotein
Abstract
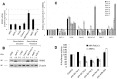
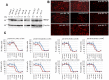
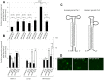
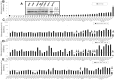
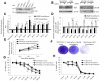
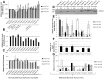
Overexpression of ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2 (RRM2), involved in deoxyribonucleotide synthesis, drives the chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer to nucleoside analogs (e.g., gemcitabine). While silencing RRM2 by synthetic means has shown promise in reducing chemoresistance, targeting endogenous molecules, especially microRNAs (miRNAs), to advance chemotherapeutic outcomes has been poorly explored. Based on computational predictions, we hypothesized that the let-7 tumor suppressor miRNAs will inhibit RRM2-mediated gemcitabine chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Reduced expression of the majority of let-7 miRNAs with an inverse relationship to RRM2 expression was identified in innately gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cell lines. Direct binding of let-7 miRNAs to the 3' UTR of RRM2 transcripts identified post-transcriptional regulation of RRM2 influencing gemcitabine chemosensitivity. Intriguingly, overexpression of human precursor-let-7 miRNAs led to differential RRM2 expression and chemosensitivity responses in a poorly differentiated pancreatic cancer cell line, MIA PaCa-2. Defective processing of let-7a precursors to mature forms, in part, explained the discrepancies observed with let-7a expressional outcomes. Consistently, the ratios of mature to precursor let-7a were progressively reduced in gemcitabine-sensitive L3.6pl and Capan-1 cell lines induced to acquire gemcitabine resistance. Besides known regulators of let-7 biogenesis (e.g., LIN-28), short hairpin RNA library screening identified several novel RNA binding proteins, including the SET oncoprotein, to differentially impact let-7 biogenesis and chemosensitivity in gemcitabine-sensitive versus -resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Further, LIN-28 and SET knockdown in the cells led to profound reductions in cellular proliferation and colony-formation capacities. Finally, defective processing of let-7a precursors with a positive correlation to RRM2 overexpression was identified in patient-derived pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) tissues. These data demonstrate an intricate post-transcriptional regulation of RRM2 and chemosensitivity by let-7a and that the manipulation of regulatory proteins involved in let-7a transcription/processing may provide a mechanism for improving chemotherapeutic and/or tumor growth control responses in pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Goan YG, Zhou B, Hu E, Mi S, Yen Y (1999) Overexpression of ribonucleotide reductase as a mechanism of resistance to 2,2-difluorodeoxycytidine in the human KB cancer cell line. Cancer Res 59: 4204–7. - PubMed
-
- Itoi T, Sofuni A, Fukushima N, Itokawa F, Tsuchiya T, et al. (2007) Ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2 mRNA expression in pretreatment biopsies obtained from unresectable pancreatic carcinomas. J Gastroenterol 42: 389–94. - PubMed
-
- Zhou B, Mo X, Liu X, Qiu W, Yen Y (2001) Human ribonucleotide reductase M2 subunit gene amplification and transcriptional regulation in a homogeneous staining chromosome region responsible for the mechanism of drug resistance. Cytogenet Cell Genet 95: 34–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

