Roles of cytochrome P4502E1 gene polymorphisms and the risks of alcoholic liver disease: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 23335995
- PMCID: PMC3545986
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054188
Roles of cytochrome P4502E1 gene polymorphisms and the risks of alcoholic liver disease: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Previous studies investigating the association between cytochrome P4502E1 (CYP2E1) polymorphisms and the risk of alcoholic liver diseases (ALD) have yielded conflicting results. Thus, a meta-analysis was performed to clarify the association between CYP2E1 polymorphisms and the risks of ALD.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted to identify the relevant studies. The fixed or random effect model was selected based on the heterogeneity test among studies. Publication bias was estimated using Begg's funnel plots and Egger's regression test.
Results: A total of 27 and 9 studies were finally included for the association between the CYP2E1 Pst I/Rsa I or Dra I polymorphisms and the risks of ALD, respectively. Overall, the combined results showed that homozygous genotype c2c2 was significantly associated with increase risk of ALD in worldwide populations (c2c2 vs. c1c1: OR = 3.12, 95%CI 1.91-5.11) when ALD patients were compared with alcoholics without ALD. Significant associations between CYP2E1 Pst I/Rsa I polymorphism and ALD risk were also observed in Asians (c2c2 vs. c1c1: OR = 4.11, 95%CI 2.32-7.29) and in Caucasians (c2c2/c1c2 vs. c1c1: OR = 1.58, 95%CI 1.04-2.42) when ALD patients were compared with alcoholics without ALD. However, subgroup analysis stratified by ALD types showed that CYP2E1 Pst I/Rsa I polymorphism was not significantly associated with the risks of alcoholic cirrhosis (ALC). No significant association was observed between CYP2E1 Dra I polymorphism and ALD risks.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis suggested that CYP2E1 Pst I/Rsa I polymorphism might be not significantly associated with advanced form of ALD (ALC), but might be significantly associated with other form of ALD such as steatosis, hepatisis, fibrosis. Furthermore, CYP2E1 Dra I polymorphism might be not significantly associated with the ALD risks. Since potential confounders could not be ruled out completely, further studies were needed to confirm these results.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
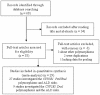

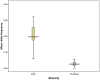

Similar articles
-
Association between CYP2E1 genetic polymorphisms and urinary cancer risk: a meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 18;8(49):86853-86864. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20993. eCollection 2017 Oct 17. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29156840 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic polymorphisms of cytochrome p4502E1 and susceptibility to alcoholic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma in a white population: a study and literature review, including meta-analysis.Mol Pathol. 2000 Apr;53(2):88-93. doi: 10.1136/mp.53.2.88. Mol Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10889908 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of CYP2E1 polymorphisms in liver carcinogenesis.Dig Liver Dis. 2017 Jan;49(1):77-83. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2016.08.114. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Dig Liver Dis. 2017. PMID: 27637154
-
Associations between the tumor necrosis factor-α gene and interleukin-10 gene polymorphisms and risk of alcoholic liver disease: A meta-analysis.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2016 Sep;40(4):428-39. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2015.10.007. Epub 2015 Dec 4. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26656007 Review.
-
Does CYP2E1 RsaI/PstI polymorphism confer head and neck carcinoma susceptibility?: A meta-analysis based on 43 studies.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Oct;95(43):e5156. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005156. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27787372 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances and Controversies in Acute Alcohol-Related Hepatitis: From Medical Therapy to Liver Transplantation.Life (Basel). 2023 Aug 24;13(9):1802. doi: 10.3390/life13091802. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mini-review of the rodent models for alcoholic liver disease: shortcomings, application, and future prospects.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021 May 10;10(3):523-530. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfab042. eCollection 2021 May. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34141166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethnic differences in presentation and severity of alcoholic liver disease.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015 Mar;39(3):566-574. doi: 10.1111/acer.12660. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015. PMID: 25702770 Free PMC article.
-
The TNF-α rs361525 and IFN-γ rs2430561 polymorphisms are associated with liver cirrhosis risk: a comprehensive meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 14;14:1129767. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1129767. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37122734 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of isoflavones on alcoholic liver diseases: Computational approaches to investigate the inhibition of ALDH2 with isoflavone analogues.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Feb 27;10:1147301. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1147301. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36923641 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

