Human CD3γ, but not CD3δ, haploinsufficiency differentially impairs γδ versus αβ surface TCR expression
- PMID: 23336327
- PMCID: PMC3585704
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-14-3
Human CD3γ, but not CD3δ, haploinsufficiency differentially impairs γδ versus αβ surface TCR expression
Abstract
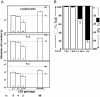
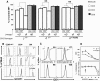
Background: The T cell antigen receptors (TCR) of αβ and γδ T lymphocytes are believed to assemble in a similar fashion in humans. Firstly, αβ or γδ TCR chains incorporate a CD3δε dimer, then a CD3γε dimer and finally a ζζ homodimer, resulting in TCR complexes with the same CD3 dimer stoichiometry. Partial reduction in the expression of the highly homologous CD3γ and CD3δ proteins would thus be expected to have a similar impact in the assembly and surface expression of both TCR isotypes. To test this hypothesis, we compared the surface TCR expression of primary αβ and γδ T cells from healthy donors carrying a single null or leaky mutation in CD3G (γ+/-) or CD3D (δ+/-, δ+/leaky) with that of normal controls.
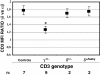
Results: Although the partial reduction in the intracellular availability of CD3γ or CD3δ proteins was comparable as a consequence of the mutations, surface TCR expression measured with anti-CD3ε antibodies was significantly more decreased in γδ than in αβ T lymphocytes in CD3γ+/- individuals, whereas CD3δ+/- and CD3δ+/leaky donors showed a similar decrease of surface TCR in both T cell lineages. Therefore, surface γδ TCR expression was more dependent on available CD3γ than surface αβ TCR expression.
Conclusions: The results support the existence of differential structural constraints in the two human TCR isotypes regarding the incorporation of CD3γε and CD3δε dimers, as revealed by their discordant surface expression behaviour when confronted with reduced amounts of CD3γ, but not of the homologous CD3δ chain. A modified version of the prevailing TCR assembly model is proposed to accommodate these new data.
Figures
References
-
- Siegers GM, Swamy M, Fernández-Malavé E, Minguet S, Rathmann S, Guardo AC. et al.Different composition of the human and the mouse gammadelta T cell receptor explains different phenotypes of CD3gamma and CD3delta immunodeficiencies. J Exp Med. 2007;204(11):2537–44. doi: 10.1084/jem.20070782. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Regueiro JR, López-Botet M, De Landazuri MO, Alcami J, Corell A, Martín Villa JM, Vicario JL, Arnaiz-Villena A. An in vivo functional immune system lacking polyclonal T-cell surface expression of the CD3/Ti(WT31) complex. Scand J Immunol. 1987;26(6):699–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02306.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Perez-Aciego P. Caracterización clínica, inmunologica y molecular de una inmunodeficiencia familiar por defecto de expresión del receptor para antígeno del linfocito T, PhD thesis. 12 de Octubre Hospital, Madrid, Immunology Department. 1992.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

